USB-C charging: discover its secrets! ⚡️🔌In 2025.
USB Type-C is the most flexible connection for notebooks and smartphones. The most important thing about its multiple capabilities is that it works as a charging port for battery-powered devices. USB-C ought simplify everything: one port, one cable, one power supply for all devices, from computers to smartphones, tablets, headphones and other peripherals. ⚡
So much for the theory, which always sounds simple with USB. The reality is a bit more confusing.
Not all of them power supplies USB-C ports are suitable for all devices. Not all Type-C ports can be used to charge devices quickly or even for charging. And not all Type-C cables guarantee reliable power transmission. 🔌
This guide will give you an overview of the technical possibilities of Type-C charging and recommend suitable power supplies for all devices. If you'd rather skip all the details and just find out which cables are worth your money, be sure to check out our selection of the best USB-C cables. We conduct practical tests that go far beyond most other sources on the market. red. 💰
USB Type-C: The standard connection for charging
IDG
Almost all devices mobiles can now be charged via USB Type-C: For smartphones, Apple was the last major manufacturer to make the switch from the proprietary Lightning connector to USB-C last year with the iPhone 15. 📱
Apart from that, there are only a few very inexpensive smartphones that still rely on micro USB as a charging port. The situation is similar for tablets, where market leader Apple already favoured USB-C over Lightning three years ago with the iPad 9. You will hardly find devices without USB-C for headphones, e-book readers and portable speakers.
Only laptops still have numerous models that do not use Type-C for charge the battery: Often, these are older entry-level model series. However, it is increasingly common that USB-C is not the major connection for charging.
Even though powerful gaming and multimedia laptops have USB-C, they also have a dedicated power connection with a higher charging capacity that matches the supplied power supply. Business laptops with a USB-C port and a power supply often still have the pin connector so that companies can continue to use power supplies from discontinued models.
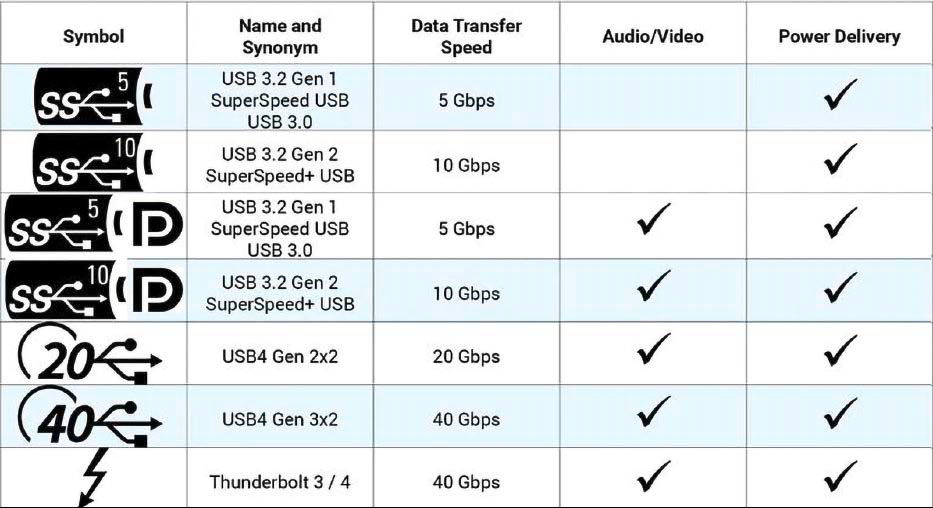
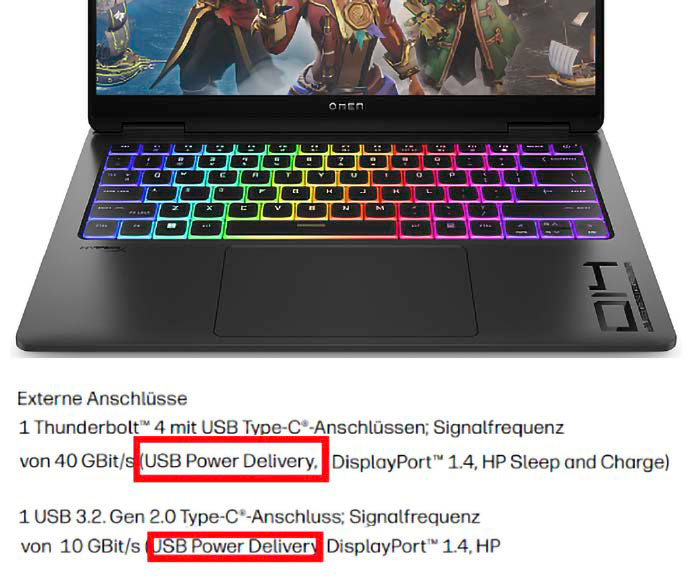
A Type-C connector on a laptop doesn't always handle power delivery either. The only way to find out if a Type-C connector is capable of power delivery is to check the technical specifications. A Type-C port with Thunderbolt supports charging in any case.
Advantages of USB-C Power Delivery
The triumph of Type-C is easy to explain, as the connection offers numerous advantages for users and manufacturers:
- The cables can be connected quickly and easily because the connector is symmetrical and cannot be placed upside down. 🔄
- The socket takes up little space, allowing devices to be lighter and flatter. 🏋️♂️
- And since Type-C can handle data and video transmission as well as charging, ideally a single cable is all that's needed between your computer and peripherals, keeping your desk clutter-free. 🗄️
IDG
In addition, devices can be charged faster with USB-C: Micro USB power supplies only deliver up to 10 watts, while chargers with a Type-A connection typically deliver between 15 and 18 watts. On the other hand, Type-C supports the improved USB Power Delivery (PD) transmission protocol, which typically enables charging capacities of up to 100 watts and even up to 240 watts in the current version. 🚀
However, this does not apply to all Type-C connections, devices and cables: even if everything fits together mechanically, not every combination has to provide the optimal charging power, for example because different levels of the Power Delivery standard are supported or because the devices and power supplies do not implement the standard correctly.
USB-C and Power Delivery: How the charging technology works
The technical basis for charging via USB-C is the USB Power Delivery (USB PD) standard. This specifies voltage levels of 5 to 48 volts and currents of 3 or 5 amps in so-called "power profiles" or "power rules". Depending on the power supply, power cable and device, charging capacities ranging from 10 to 240 watts are possible.
A typical 30-watt smartphone power supply, for example, offers power profiles for 15, 27, and 30-watt charging capacities, while a laptop power supply also offers power profiles for 45, 60, 65, or 100 watts.
Before transmission begins, the power supply (source) and the consumer (load) agree on the required voltage and current: First, the power supply checks the cable to see if it can transmit up to 3 or 5 amps and provides a basic voltage of 5 volts.
It then informs the consumer what additional voltages it can supply. The consumer responds which one they need so that both can agree on a suitable power profile. 🤝

Ugreen
Ideally, any USB-C power supply will charge the device equipped with a Type-C charging port with optimal performance and as quickly as possible. Even if the power supply does not fully meet the device's requirements, it should still provide a minimum charging power, even if the charging process takes longer. ⏳
On the other hand, using a power supply that offers a higher output than the device requires does not speed up the charging process, since the consumer cannot call upon it.
Since USB PD version 3, the power supply and the consumer can adjust voltage and current more dynamically. To do this, both must support the optional standard extension PPS (Programmable Power Supply Protocol). 📊
The device can then request voltage and current from the power supply that deviate minimally from the prescribed power profiles: this speeds up the charging process, but can also ensure that the battery is less stressed during charging or that a smartphone or notebook receives the appropriate charging power in real time based on the current system load. 🔧
Labels like Fast Charge or Super Fast Charge 2.0 on Samsung smartphones, for example, indicate support for PPS.
How to find out if a power adapter fits your device
The easiest way to do this is to use the manufacturer's recommended power adapter for charging. This is common for laptops, as new devices are supplied with a suitable power supply. ✔️
Smartphones and tablets now often do not come with a power adapter in the sales box: you can purchase the correct charger from the device manufacturer.
USB-C should make this investment unnecessary and put an end to the confusion of power adapters that only serve one device. A power supply that can charge all your devices without problems is therefore ideal. 🏆
To do this, the power supply and the device must have a USB-C connection and support USB Power Delivery – you should be able to find this information in the technical specifications, often as an abbreviation such as “PD” or “PPS”. If the power supply or the device does not support USB PD despite Type-C, charging can start, but only at 15 watts.
In order for you to be able to charge all your devices with a single power supply, it must have enough charging power for the most powerful device and appropriate power profiles for devices with lower power requirements.
Generally, a laptop is the device that requires the most charging power: ultra laptops mobiles Typically, laptops require a 45 watt power supply, standard laptops require 60 watts, and particularly powerful laptops require 100 watts. 💻
On the other hand, for smartphones, tablets and portable speakers or headphones, 30 watts or less is sufficient.
To ensure that a USB-C laptop power supply charges other devices mobiles, must support power profiles for 15 and 27 watts via USB-PD.
With third-party power supplies, you'll often find a list of other devices that can be charged by it in the technical specifications of a laptop power supply. If tablets are listed as Apple iPad Pro and smartphones – e.g. Samsung Galaxy S24 – the power supply is also suitable for smaller mobile devices.
If you want to use the power adapter that came with your laptop, check the manufacturer's website for information about its output power: If you find information like "9 volts – 3 amps", the power adapter is suitable for smartphones and tablets. These values are usually also printed on the power supply unit under "Output".
On the other hand, notebooks can also be charged with a smartphone power adapter – this is useful when travelling if you only want to take the lightest mobile charger with you. The power supply must offer at least 27 watts of charging power and a voltage of 9 volts. This is sufficient for small and light laptops.
It is best to turn off the notebook when charging, because if it draws more power during operation than the adapter delivers, the battery will be drained even when the charger is connected. However, many notebooks require 15 volts, and most require 20 volts as the charging voltage. If your smartphone power adapter provides this, the notebook can also be charged with it, but usually only slowly.
The best cable for charging via USB-C
A good USB-C cable is crucial to ensure that the charging power from the power supply to the device is stable. The cables transmit a current of up to 3 amps as standard. ⚡
This is sufficient for mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Notebooks can also be charged with up to 60 watts using such cables – this is sufficient for small and light laptops. For larger and more powerful laptops, however, charging will take longer depending on the battery size and operating load.
To charge these laptops at optimal speed via USB-C, you need a cable that can transfer 5 amps. The fast charging features Some smartphones and tablets also require a suitable cable, such as Samsung's Super Fast Charge. 🔄
IDG
These cables contain a chip, the so-called e-marker: it contains information about the capabilities of the cable, such as maximum power delivery capacity, voltage and current values, and supported charging protocols.
This chip provides that information when the power supply and consumer negotiate the optimal charging power via USB-PD, to ensure that the charger delivers the appropriate voltage and current values for the cable and the connected device. 📈
Most manufacturers usually describe the corresponding cables as “100 watt cables”. You will also often find a reference to the e-marker chip in the technical specifications.
In addition to power transfer, USB-C also supports data and image transfer: If you want to use one cable for all applications, you should pay attention to this in its description: These multifunctional cables are usually slightly more expensive than pure charging cables. Cables for Thunderbolt guarantee to support all types of USB-C transmission.
You can't know how well a charging cable transmits data: in theory, longer cables are more susceptible to voltage loss and limit current flow due to higher resistance. Thicker cables should ensure more stable transmission.
However, in practice, you cannot use this rule as a guide: the quality of a cable depends on its internal manufacturing. 🔍
Basic advice: Buy cables for higher charging capacities from reputable suppliers such as Anker, Belkin or Ugreen. They are reliable and usually cheaper than corresponding offers from the laptop or smartphone manufacturer.
Multi-port chargers: One power source for all your devices
A single power supply is usually not enough for a large number of devices: you often want to charge different devices at the same time via USB-C. That's why there are power supplies with multiple USB-C and USB-A ports, which can be used, for example, to charge a notebook, smartphone and headphones in parallel. This is also useful when you're travelling and only have one socket available on the train, for example. 🚄
When choosing, you should first consider how many devices you want to charge at the same time and on which ports: there are multiple power supplies with numerous connection combinations, so you should always be able to find a suitable model.
Devices with two USB-C ports start at around $20, while prices with three Type-C ports start around $40. In most cases, power supplies also have a Type-A charging port in addition to the USB-C outputs.
You should also decide on the maximum charging power that the multi-power supply should have: up to 45 watts is sufficient for a smartphone and headphones. If you also want to charge a laptop, at least 60 watts is recommended.
USB power supplies with multiple connections:
| Manufacturer | Product from the manufacturer | Price (euros) | Maximum charging power (watts) | Type C Number | Type A Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anker | Prime (GaN) | 80 | 100 | 2 | 1 |
| Armature | 735 (Nano II) | 35 | 65 | 2 | 1 |
| Armature | 735 Prime (GaN) | 50 | 65 | 2 | 1 |
| Armature | 323 | 20 | 32 | 1 | 1 |
| Belkin | Boost Charge Pro | 40 | 65 | 2 | – |
| Ugreen | Nexode Pro Mini (GaN) | 100 | 160 | 3 | 1 |
| Ugreen | Nexode (GaN) | 30 | 65 | 2 | 1 |
| Ugreen | Nexode (GaN) | 55 | 100 | 3 | 1 |
| Ugreen | Nexode Pro Mini (GaN) | 45 | 65 | 2 | 1 |
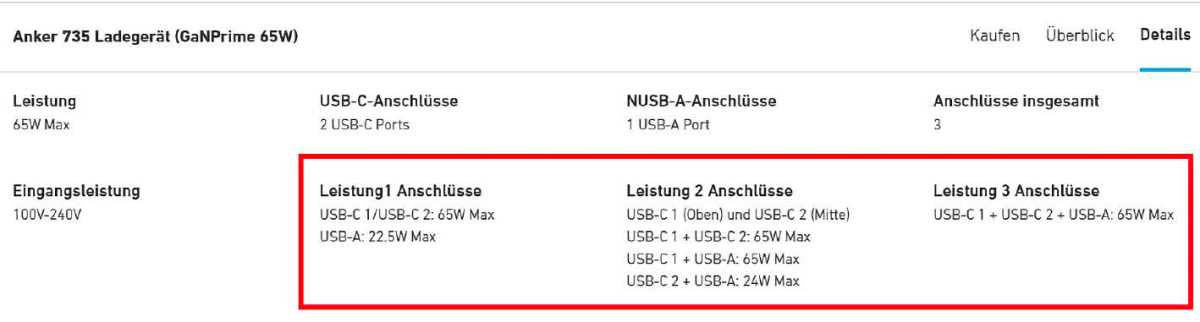
It is important to know how to distributes power between individual ports: The maximum charging power specified by the manufacturer usually applies to all ports together, only to the combination of certain ports, or only if a single port is occupied.
For example, if you choose a 65-watt power supply because you also want to charge your laptop, it will typically only deliver this charging power if a single USB-C port is occupied. If you charge another device on the second Type-C port, the power will be split between 45 watts on one port and 20 watts on the other, and the laptop will charge more slowly. ⏲️
If all ports on a three-port power supply are occupied by consumers, the power on a single port can drop even further. Also, not all Type-C connections on the power supply have to deliver the same charging power: for example, the laptop can only receive up to 65 watts on port 1. If you connect it to port 2, it will only receive up to 45 watts.
Therefore, you should check the technical specifications of a model on the power supply supplier's website before purchasing: well-known manufacturers such as Anker o Belkin lists the charging power offered by individual ports with single or multiple connections. 📊
The desired power supply should support USB-C Power Delivery and preferably also PPS.
Many manufacturers promote more expensive models with the abbreviation "GaN«: This refers to the semiconductor material gallium nitride, from which, for example, converters in corresponding power supplies are made: they operate very efficiently without overheating, which allows for small power supplies with a high load capacity.