Command Prompt: 5 Quick Tricks to Fix Windows ⚡🖥️
I can't remember a single month I've been using Windows without encountering some problem. Whenever something goes wrong, I turn to the built-in Windows tool: the Command Prompt. It may seem intimidating at first, but once you get the hang of it, it becomes a powerful ally in troubleshooting.
1. Repair Corrupt System Files
When my computer starts to crash, displaying the dreaded Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), becomes slow or exhibits strange behavior, the first thing I do is check for corrupted system files. Fortunately, the Command Prompt makes this process easy. I open the console and type sfc /scannow, which automatically scans and repairs corrupted files or missing from the system.
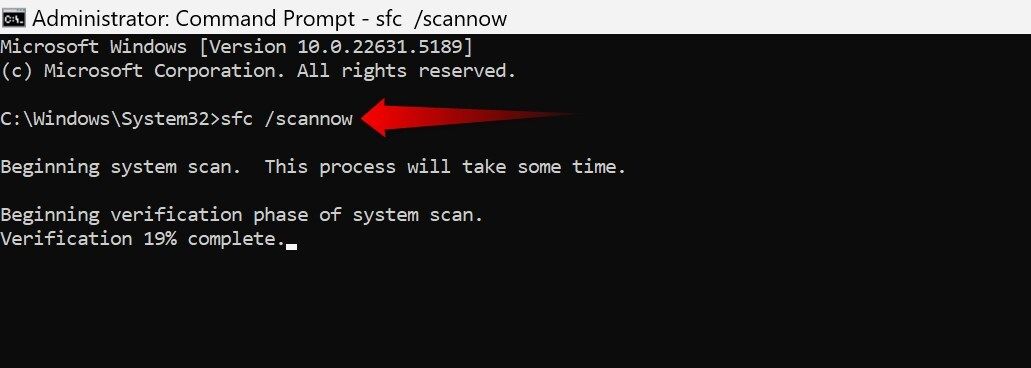
Upon completion, a report is generated detailing the errors found and whether they were repaired. If the problem persists, use the DISM tool to repair the Windows image by typing DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth. Then I repeat sfc /scannow, and this usually solves the problem.
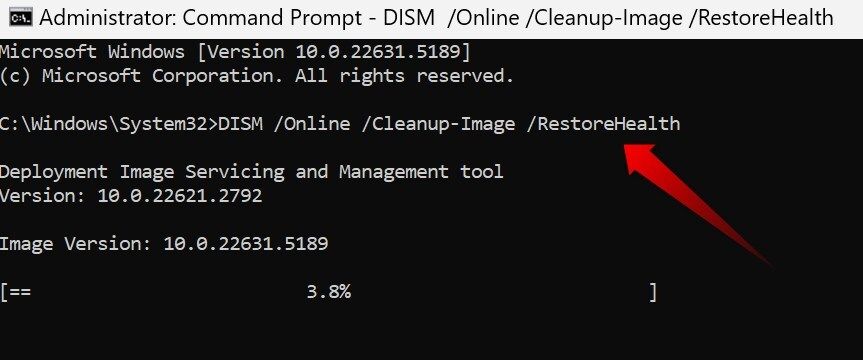
These commands are my go-to for troubleshooting most operating system issues with Command Prompt.
2. Troubleshooting Network Connectivity Problems
We've all experienced internet outages just when we need it most. Whether the Wi-Fi drops out, the signal is slow, or the connection drops completely, before blaming my provider, I run a few key checks from the Command Prompt to rule out local issues.
These commands are usually my first steps:
- ipconfig /release and ipconfig /renew: Release the current IP address and request a new one from the router.
- ipconfig /flushdns: Clean up corrupt or obsolete DNS entries to get fresh records.
- netsh int ip reset: Resets the TCP/IP stack to its original state. I only use this as a last resort.
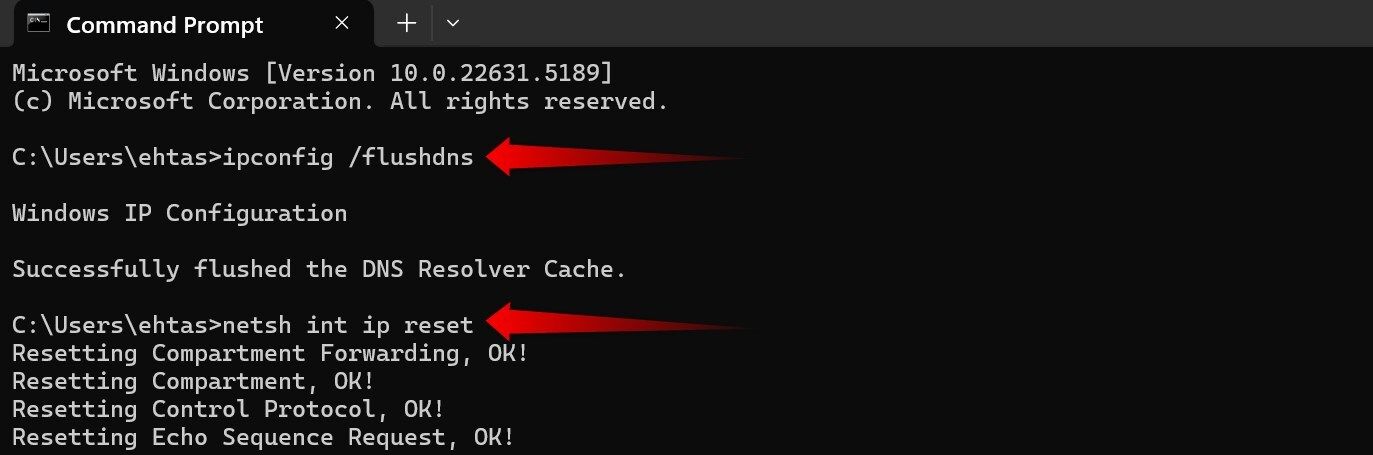
These basic commands usually resolve most connectivity issues. For more in-depth analysis, there are advanced commands that can help you diagnose your network in greater detail.
Related
Internet not working? 10 troubleshooting tips
Did your internet suddenly stop working? Here's how to fix it.
3. Examine and Diagnose Hard Drive Errors
Windows has the Check Disk tool, which is part of my regular maintenance routine. This scan detects corrupted files, bad sectors, and file system errors that, if ignored, can cause freezes or corruption.
To use it, I open the Command Prompt and type chkdsk C: /f /r. Where C: is the unit to be checked, /F fix bugs and /r locates bad sectors and recovers readable data.
If you notice frequent errors, employment wmic diskdrive get status to assess the disk's health. An "OK" result indicates a good disk, but "Previous Fail" or "Unknown" indicate a possible failure. In that case, I always back up my important data immediately.
4. Force Close Non-Responsive Apps
When an application freezes, the first thing to do is open the Task Manager. If it's not responding, use the command taskkill from the Command Prompt, which terminates difficult processes.
To close a specific app, type taskkill /IM processname.exe /F. For example, to close Notepad: taskkill /IM notepad.exe /F. Here, /IM indicates the name of the image/process and /F force closure.
You can also close multiple processes at once by separating them with more labels. /IM, For example: taskkill /IM app1.exe /IM app2.exe /F. Just add the correct names.
5. Troubleshoot Microsoft Store and Apps
I use several apps from the Microsoft Store, but sometimes they stop working, don't update, or the store itself crashes. When this happens, clearing its cache is usually the quick fix.
Open Command Prompt and type wsreset.exeA black window will appear for a few seconds, and then the store will open automatically, ready to use.
If the issue persists, you can also reinstall or re-register Microsoft Store apps for all users to resolve persistent issues.
The Command Prompt isn't an outdated relic; I still use it daily to troubleshoot Windows problems. Now that you know how to solve problems without complicated interfaces, the next time your PC crashes, try this powerful black window! 🚀💻