Avoid these bad habits on your PC
Avoid these bad habits on your PC.
Nothing lasts forever, especially technology, but your PC can last for quite a few years if you handle it properly.
These are the worst things you can do to a PC without even realizing you're doing it wrong.
1. Ignoring overheating issues
(Photo: Iammotos/Shutterstock)
Heat is your PC's mortal enemy.
If you use your PC intensively, the processor It may slow down, throttle to maintain reasonable temperatures, or even shut down completely.
Operating at high temperatures for long periods of time can shorten the life of your processor, fans and all that, not to mention, causes your PC to be loud and sizzling to the touch.
For desktop PCs, the alternative is quite simple: make sure your room has a suitable breeze flow, with enough vents and fans to keep the air clear moving through the elements.
Keep it away from narrow cabinets and other spaces that capture heat.
PCs laptops, on the other hand, require a little more caution.
Its portability creates several bad habits, such as placing it on a blanket or other plush area.
This disables the air flow under the notebook and possibly through the laptop (if the cover covers the vents).
Whenever possible, use your notebook on a flat area (where the rubber feet usually lift it off the desk), or at least make sure your lap is free of blankets and other things that might block the air flow.
Lap desks are a good way to keep things cool.
On the other hand, from that, it is apply exactly the same rules apply to notebooks as to desktops: don't leave them in hot places (like a car on a sunny day) and blow off the dust occasionally.
If you overclock, be careful enough to monitor those voltages and temperatures.
It is also always a good idea to monitor the temperature of the central heating unit. prosecution just in case.
2. Letting dirt, dust and liquids run wild
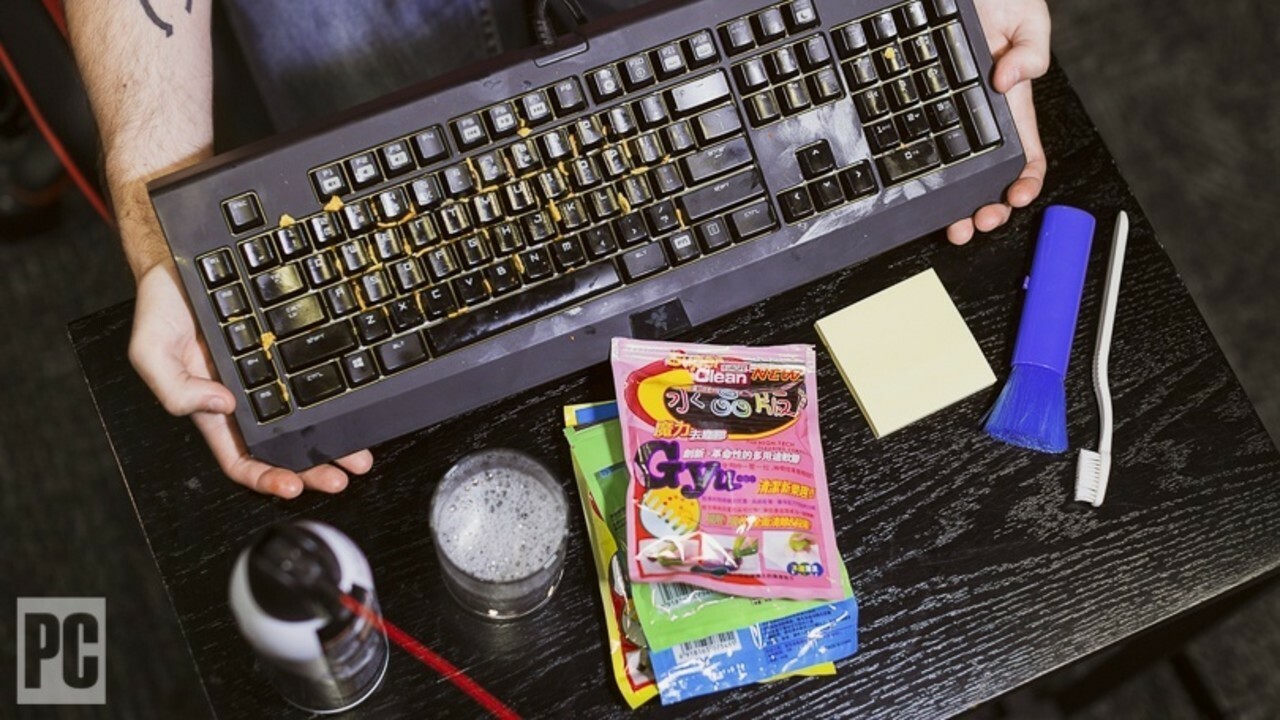

(Photo: Zlata Ivelva)
All PCs accumulate a little dust over time, heating up the media and causing the fans to work harder.
While cleaning it regularly can help, you also want to prevent things from getting onto your PC in the first place.
For example, cigarette smoke and pet hair will exacerbate those problems, and putting your desktop PC on the floor will ensure that more dust, hair, and debris will be drawn in through the doorway.
And if you have a doormat on the floor, it's probably blocking the fan power supply input.
Keep your PC on a desk or other high place, if possible, and make sure there are filters on your intake fans.
Next, do not eat or drink near your PC, or at least be careful when doing so.
Put crumbs in it keyboard Not only is this disgusting, but it can also damage switches or make some keys harder to press.
And I'm sure you've heard enough horror stories about people spilling coffee on their PCs. laptops, which can destroy it.
Even well-thought-out moves, like wiping down the screen with Windex, can get liquid in where it shouldn't (plus, Windex is pretty harsh on your screen). monitor). Spray your detergent screen slowly on a microfiber cloth, not on the screen, and don't go crazy, a little does a lot.
3. Driving your laptop without caution
(Photo: Ivan Michailovich/Shutterstock)
As the PCs While desktop computers have the pomp of sitting comfortably in your office, notebooks are subject to all kinds of abuse.
And the more you abuse it, the more likely you are to do little harm.
I've seen people lift laptops by the screen, open the hinge from the side with great force and throw his PC onto the sofa from the other side of the room.
(Sure, a couch is pretty slow, but one day, you'll miss it and regret it.)
¡://mastertrend.info/service/cambio-pantalla-notebook/» data-wpil-monitor-id=»285″>notebook or a gap in the structure.
But if your notebook You have a traditional spinning hard drive instead of an SSD, dropping or shaking the PC, especially if the drive is active at the time, can cause your boot to dislocate or touch the disk surface.
It's not popular, but if that happens, you're going to have a bad day, especially if you didn't back up your data.
His notebook It is an expensive property, so it is essential that you treat it as such.
4. Mishandling your old battery

(Illustration: ST.art/Shutterstock)
Given that the your notebook battery It starts with “eight hours of battery life” but does not guarantee that it will continue this way for a lifetime.
Batteries degrade over time – you might get eight hours on a full charge when you first buy it, but after a few years, that can degrade to six or seven hours.
There's no way to escape this doom, but you're probably degrading it much faster than necessary if you're always using your laptop at 0%.
Follow our tips for better battery management and check the battery health report at Windows to track battery charging history.
To increase the long-term health of your battery, it is preferable to carry out superficial discharges and recharge it frequently.
Don't stress too much about it - if you're on a plane and need to work, an occasional discharge won't kill your battery, but after a while, it's better to mess around with regular charging than to run it dry.
However, you should be concerned if your battery is swollen.
If your battery is so bulky that it pushes against the frame of your notebook, creating a gap between the frames, you should stop using your computer now and (as safe) replace the battery to prevent explosive rupture.
At the time you replace the battery, look for an original or similar brand.
Poor quality batteries will, at best, not hold a charge effectively well, and at worst, can be dangerous.
The same applies to third-party chargers: just stick to the official developer's offering or, in the case of notebooks that charge via USB-C, a certified USB-PD charger.
5. Ignoring electrical safety
(Illustration: jakkrit pimpru/Shutterstock)
Your PC consumes an extraordinary amount of power and is susceptible to damage from power surges - small, temporary increases in voltage coming through the power line.
This can happen after power outages, when you turn on another high-capacity device in your home, or thanks to a red unreliable electrical supply at its entrance.
The power supply in your PC includes some basic surge protection, but you'll get much longer-lasting protection from a dedicated surge protector.
Keep in mind that this is different from a power strip, which provides multiple outlets without surge protection.
Make sure to replace it every three to five years, as that protection wears out over time; if yours is old, it may not offer any protection at all.
Keep in mind that surge protectors will not protect against high voltage spikes (such as lightning), but they can protect you against smaller surges and increase the lifespan of your PC.
You can also invest in a Nobreak or (UPS).
This device has a backup battery inside that prevents your PC from losing data during a sudden power outage.
The notebooks They require a little more caution due to their portability.
While the power cord of a desktop PC remains stationary for years, the cord of your notebook It accompanies him everywhere, subject to dislocations, strong pulls on the frame and other poor handling.
Not only can this make the cord unreliable, but it can also pose a fire hazard, so always unplug the charger from the socket, not the cord.
6. Tightening the cables and ports

Photography: Aleksandrs Muiznieks/Shutterstock
While damaging a USB port or cable is not as risky as mishandling the adapter current, it can still cause avoidable damage to your PC.
This may seem obvious, but don't force cables into ports if they don't slide in properly (I once knew someone who forced a USB cable into a FireWire port and broke both).
Likewise, if you leave a little connected, be careful not to bend it.
If you have a flash drive in your computer's USB port, notebook, using your laptop with your legs crossed can bend the flash drive and damage the drive, the port, or both.
And with USB ports so expensive on computers, laptops Today, you finally won't want to ruin one of them.
The same goes for your cables.
If you regularly make sharp bends all over the place, you are much more likely to break the internal connection, which can result in the cable becoming brittle or useless.
Keep them away from hungry little ones and pets who might chew the plastic, and when you roll them up, avoid wrapping them too tightly.
Fortunately, a damaged cable is cheap to replace compared to your PC, but why waste money when it's not necessary?
7. Surfing the Internet without protection

(Photo: cyano66/Getty Images)
Contrary to popular belief, being “down to earth,” while highly appreciated, should not be your only protection against software malicious.
Even legitimate sites can be infected with software malicious and pass those inconveniences on to you, so being careful won't always save you.
En su rincón, debe utilizar un antivirus en su PC.
Fortunately, the internal feature of Windows Microsoft's Security has become quite good, after a few years of below-average scores.
Just leave it on and let it do its job.
If you want added protection, Malwarebytes Anti-Malware He is a bit more bellicose with his protection, and I found that he discovers several things that Google Chrome and Windows Security come to the fore.
The free version is fine if you just want to perform an occasional scan, but the paid version includes always-on anti-exploit features that block potentially harmful sites before they reach your screen.
When used in conjunction with a classic antivirus like Windows Security, it's going to be pretty well set up for protection.
Aside from that, other basic security practices still apply: keep your software up to date (both Windows and the programs you use), use a good password manager (instead of using the same password everywhere), and learn to spot phishing scams. Don't pirate software (which often has malware inside) and keep your network secure. Wi-Fi of your home secure with a WPA2 password.
It may seem trivial, but a bad piece of malware or ransomware can do you quite a bit of damage, so check out our guide on how to do it. virus removal for many more tips.