Fix Ubuntu: Fixed Wi-Fi in 2 min ⚡️🔧
Ubuntu is one of the favorite systems for Linux enthusiasts due to its stability, security, and user-friendly interface. However, even the most reliable systems can experience issues. If you've ever been stuck troubleshooting startup errors, Wi-Fi issues, or other glitches, these tips will be very helpful. 🚀
Ubuntu does not start correctly
Boot problems in Ubuntu can appear as black screens, GRUB errors, or messages like "initramfs" or "BusyBox." This is often due to misconfigured bootloaders, corrupted file systems, or hardware incompatibilities. A good place to start is by checking the system logs with:
journalctl -b
This command displays the logs of the current boot session, helping to identify errors in the process. For problems related to GRUB or the boot loader, the Boot-Repair tool is very useful:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair sudo apt update sudo apt install -y boot-repair boot-repairThis utility can automatically repair or reinstall GRUB, fixing common boot issues. For a complete guide, I recommend checking out my detailed tutorial on how to repair boot in Ubuntu. 💡
Wi-Fi Problems on Ubuntu
Wi-Fi issues in Ubuntu are often caused by driver incompatibilities, power management settings, or hardware recognition issues. If you're not detecting networks, experiencing frequent disconnections, or experiencing slow speeds, first check if Ubuntu recognizes your wireless adapter with:
nmcli device
This command lists the active network interfaces and their status. If the adapter appears but doesn't connect, it's likely a driver issue. Updating or installing the drivers may resolve this issue:
sudo apt update sudo apt install [driver-name]For a complete solution, check out my detailed guide on how to fix Wi-Fi problems in Ubuntu. 📡
Problems installing software on Ubuntu
The software installation In Ubuntu, it's usually straightforward, until dependency errors, broken packages, or Snap installation failures appear. A good starting point is to update and improve your installed packages with:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
If you're installing a .deb package and encounter dependency errors, try:
sudo apt --fix-broken install
It also prevents conflicts between package managers like Snap, Flatpak, and apt, as installing the same program via different paths can cause problems. 🛠️
Problems with graphics drivers
If you're experiencing display issues, unusual resolution, lack of hardware acceleration, or screen tearing, it's most likely a graphics driver issue. This is common with NVIDIA cards, but also affects Intel and AMD cards. Start by checking the "Additional Drivers" tab in Software & Updates. Ubuntu will usually detect your GPU and suggest proprietary drivers if available.
If nothing appears or performance is still poor, try on NVIDIA systems:
sudo ubuntu-drivers autoinstall
Then restart your computer. If you're not using NVIDIA, try switching from the open-source driver to the official driver from the manufacturer if available. 🎮
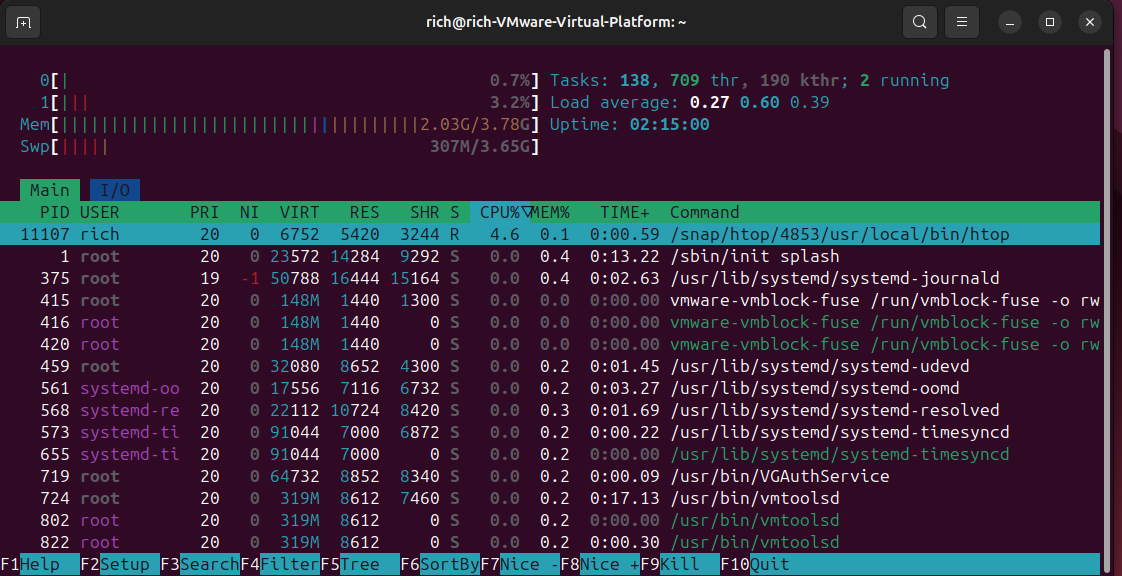
Slow performance on Ubuntu
Ubuntu can become slow for several reasons, especially if you're using heavy environments like GNOME on older hardware. A good start is to use:
htop
This tool displays real-time CPU, RAM, and active process usage. It identifies resource-intensive programs, such as certain daemons or heavy browsers. It also checks which applications start automatically and disables unnecessary ones from "Startup Applications."
If Ubuntu is still slow, consider switching to lightweight desktops like XFCE or MATE, which consume fewer resources and improve performance on older computers. ⚡
External device not recognized
You plug in a USB or SD card and nothing happens? First, check if the system detects it with:
lsblk
For additional details, use:
dmesg | tail
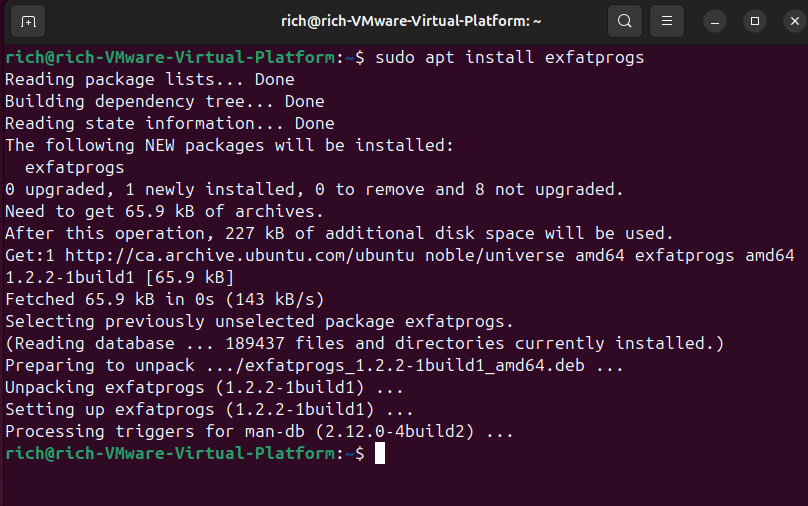
If the device appears but doesn't mount, it may lack file system support. For example, for drives formatted with exFAT, install:
sudo apt install exfatprogs
It could also be a power issue, especially with external drives. Try a different port or cable. If it's still not recognized, try the device on another computer to rule out hardware failure. 🔌
Audio not working on Ubuntu
Sound problems can be frustrating, especially after an update. First, open:
pavucontrol
This shows the output devices, input sources, and volume levels. Make sure the correct output device is selected; sometimes HDMI audio can steal sound from your speakers. If everything looks fine but there's no audio, check alsamixer:
alsamixer
Unmute channels with the key M and increase the volume with the arrow keys. Ubuntu 22.10 and later uses PipeWire, while earlier versions use PulseAudio. If in doubt, restart the services:
For PulseAudio:
pulseaudio -k
For PipeWire:
systemctl --user restart pipewire pipewire-pulse
If the problem persists, a system restart sometimes resolves temporary issues. 🔊
The system freezes or crashes
If Ubuntu crashes or becomes unstable, it could be due to drivers or overheating. Check the critical logs with:
journalctl -p 3 -xb
This command displays serious errors from the last session. If the crashes began after a kernel update, try booting to an older version from the GRUB menu. You can also test your RAM with Memtest86+ available in GRUB.
Check temperatures with:
sensors
On NVIDIA cards, switching between the free Nouveau driver and the proprietary driver may improve stability. ⚠️
Almost every problem in Ubuntu has a solution; you just need the right starting point. Whether it's fixing screens, speeding up your system, or restoring audio and external drives, a few terminal commands can save you a lot of time and frustration. And if you ever get stuck, the community Linux is a resource Invaluable. Forums, wikis, and question sites like Ask Ubuntu are full of creative solutions and support. Don't hesitate to use them! 💬✨