Headless Server: Reuse your old PC in 10 min ⚡️
Summary
- Running a headless server optimizes performance by using only the command line.
- A headless server boosts learning of Linux commands, key skills across multiple platforms.
- Managing a headless server remotely via SSH is more efficient, without the need to connect a monitor.
Do you have an old laptop or mini PC you want to repurpose? Instead of installing a desktop operating system, here's why you should turn that machine into a headless server.
What is a Headless Server?
A headless server is a computer that runs an operating system without a graphical user interface (GUI). It typically runs a dedicated server system accessible only via the command line.
This type of server was previously associated with professionals or system administrators, but today it is accessible to anyone thanks to modern and simple solutions.

Headless servers offer many advantages: improved efficiency by not consuming graphical interface resources, hands-on terminal learning, simplified remote access, and more.
Personally, I use more headless servers at home than GUI systems, as they are faster to deploy, manage, and maintain.
1. Headless Server Provides Optimal Performance
One of the main reasons to choose a headless server is to improve performance. If you're using the device for remote services, like Plex, avoid installing heavy interfaces that only consume resources.

A headless server eliminates the graphical interface and leaves only the terminal, saving RAM and processor usage. This frees up resources for services to run faster.
The advantage is huge for older or underpowered devices, as traditional operating systems with visual effects can slow them down. Using only a terminal, these older devices can be more agile and efficient.

2. Learn Practical Linux Skills Using the Command Line
One of the biggest advantages of a headless server is that it forces you to master the Linux command line, a valuable skill.

For example, in Ubuntu Desktop you can install programs with a graphical interface. On a headless server, you only have a terminal, so you must learn commands to install, configure, and remove programs.
You'll also need to use terminal text editors like nano, vim, or Emacs to modify configuration files. Personally, I use nano to edit my /etc/fstab file and add remote shares.
Estas habilidades se trasladan a diversos entornos, desde un VPS, Raspberry Pi o incluso macOS, que comparte muchas bases Unix/Linux.

3. Easily Manage Your Headless Server Remotely via SSH
A great benefit of a headless server is not having to keep it connected to a monitor. Typically, you only need a display for initial setup, then you can control it remotely.
I don't connect any monitors to my headless servers. I use SSH (Secure Shell) to manage all my systems from any computer on the network, or even from outside, using SSH tunnels or VPNs like Tailscale or WireGuard.
Controlling the server remotely with SSH allows me to manage it from anywhere: from the bedroom, the living room, the office, or even miles away.

4. Still GUI Friendly – But Different
You might think that a headless server doesn't have any GUI, but that's not entirely true.
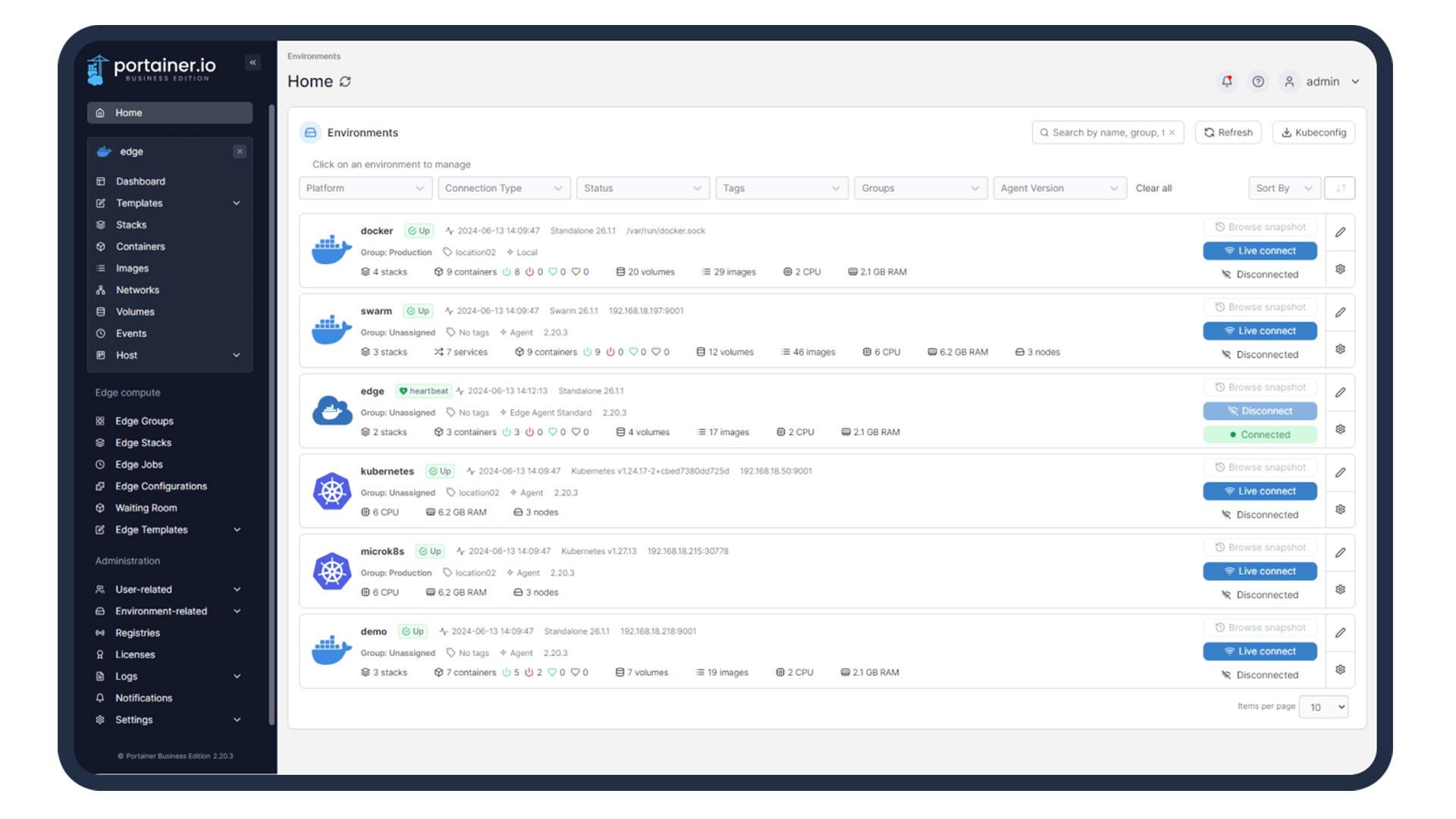
Although there is no traditional desktop, you can install web interfaces for management. For example, I use Portainer to manage my Docker containers, Proxmox for virtual machines and Unraid for storage.
These tools are managed via a web browser, offering a lightweight graphical interface without the high power consumption of a desktop operating system.
This way, you get the advantage of the GUI and save resources. This is my favorite way to manage servers because it's efficient and lightweight.
Other options include Nextcloud for storage and collaboration, and Cockpit for managing various aspects of Linux, among many others.
Remember, a headless server can have a web-based GUI and retain all the powerful features of a terminal-only system.
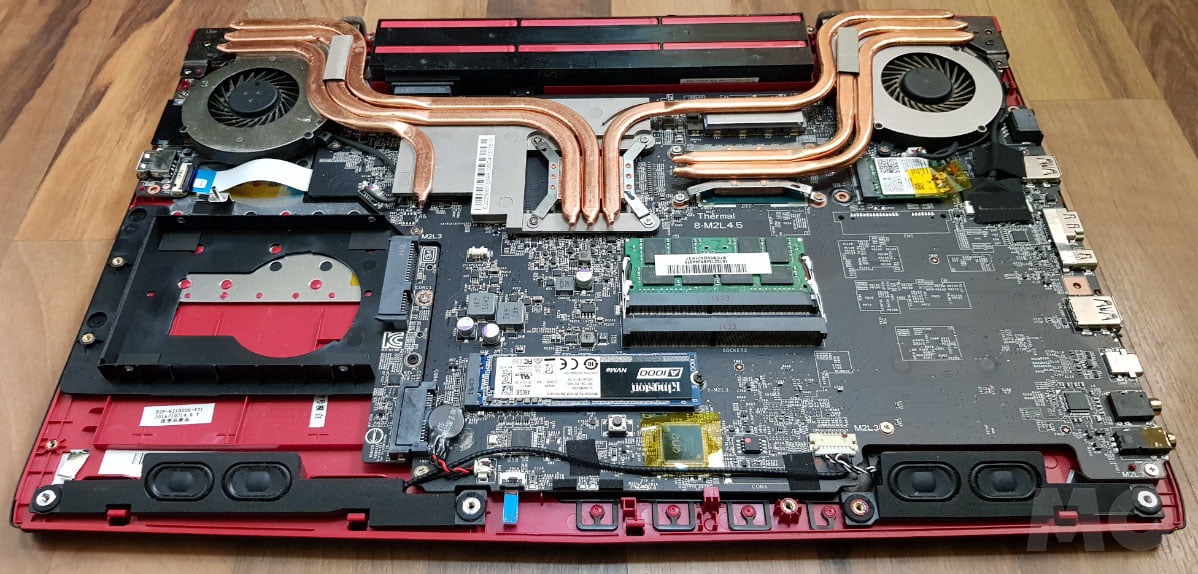
5. Works Perfectly on Old or Repurposed Hardware
If you have an old, unused computer, it could be ideal for a headless server. Web services at home don't require a very powerful computer.
I've seen people use laptops with broken screens as headless servers. You just need to configure the video output and enable SSH, and then it will work without a monitor connected.
Headless systems consume less power than desktop systems, ideal for less powerful computers. This efficiency is one of the greatest advantages of this approach, which you shouldn't ignore.

6. Ideal for Home Labs and Experimentation
A major advantage of headless servers is how easy they are to set up. They require minimal initial setup and can operate for years without problems.
Lightweight server operating systems are easy to reinstall or change, perfect for those who want to experiment. When I first started using Linux, I appreciated that my VPS was easy to restore in case of an error.
It's perfect for a home lab. My servers run Docker, virtual machines, and more, without any desktop systems. If something fails, I can reinstall it in a few hours without worry, giving me the freedom to test and develop.

Once you have your headless server up and running, don't forget to review the basic Linux commands every user should know. They're essential for managing your server effectively. Learn them or save this page for future reference! 💻✨