🔥 Local System Host Service – Lower your CPU to 10% NOW 🚀
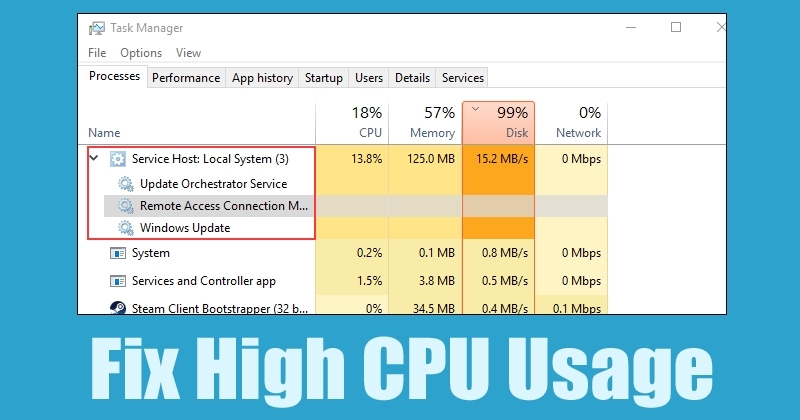
Many Windows users have experienced an issue where up to 95% of their CPU and disk are used by a process called Host Service: Local System and Host Service: Network ServiceThese two processes typically cause disk and CPU usage from the 99% to the 100%.
Many readers have asked us about the Host: LocalSystem service and its function. Well, it's a vital system process for good reason. So in this article, we'll cover everything you need to know about the Host: LocalSystem service.
What is the Host: Local System Service?
The Host: Local System service is vital and operates automatically. This process includes automatic Windows updates, background task management, IP configuration, and many other tasks. During automatic Windows updates, the Host: Local System service can also consume your internet data.

However, the Host: Local System Service runs silently and doesn't interrupt our work. Still, if your computer has less than 2GB of RAM or a low-end processor, it can ruin your entire Windows experience. This process can also cause overheating issues, affecting a laptop's battery life.
According to Windows users, the high CPU and disk usage of Host:LocalSystem Service is caused by the Windows system service known as Superfetch. But it's still a critical process that handles many tasks. The Host: Local System service typically annoys users after startup when it tries to perform multiple tasks simultaneously.
Superfetch is a technology that allows the operating system to manage random memory. Thanks to Superfetch, our applications launch quickly. Superfetch analyzes RAM usage patterns to learn what types of applications we use most often. Over time, Superfetch flags these applications, preloading them into RAM, resulting in faster app launch times.
However, we rarely need this feature, and the Superfetch service often causes high CPU and RAM usage. Therefore, the Superfetch service is the root cause of high CPU usage in Windows. To fix the high CPU usage of the Host: Local System service, we need to disable Superfetch.
How to fix high disk, CPU, and memory usage in the Host Service: Local System
Below, we'll list some simple methods to resolve the high disk usage of the Host: Local System Service. Follow the steps carefully to avoid errors. 🚀
1. Disable Superfetch
1. First, open Task Manager on your Windows 10 computer and maximize the Host Service: Local System.
2. Next, find and right-click on Superfetch and select Open services.
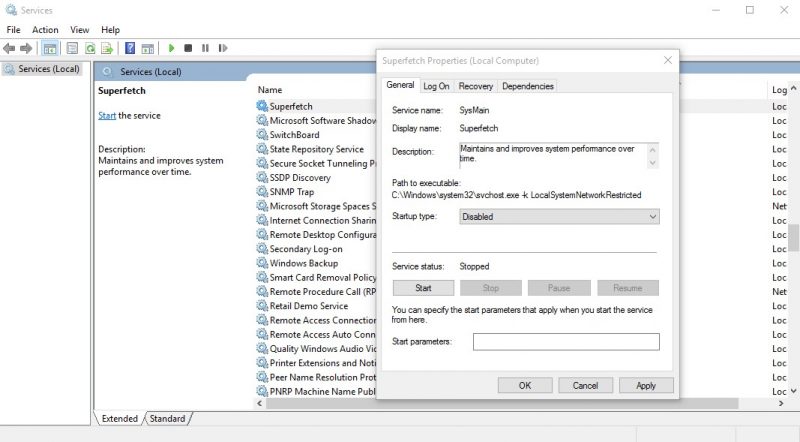
3. Now, under services, look for Superfetch. Right click on it and select Properties. In the startup type, select Disabled and click Apply.
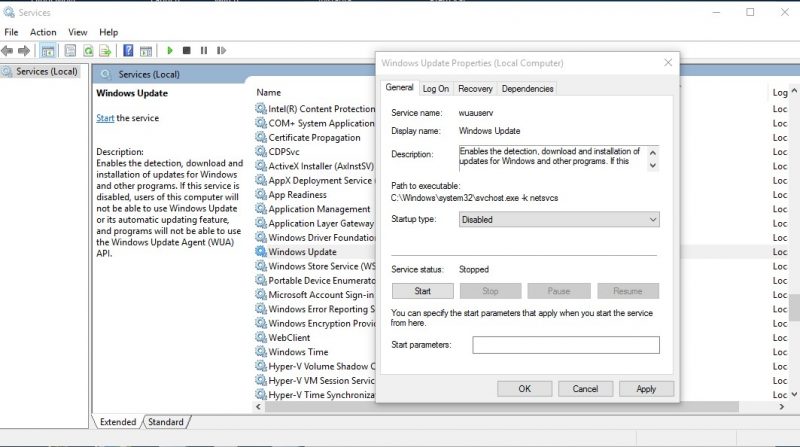
4. Then, search Windows Update, right click on it and select Properties. In the startup type, select Disable and click apply.
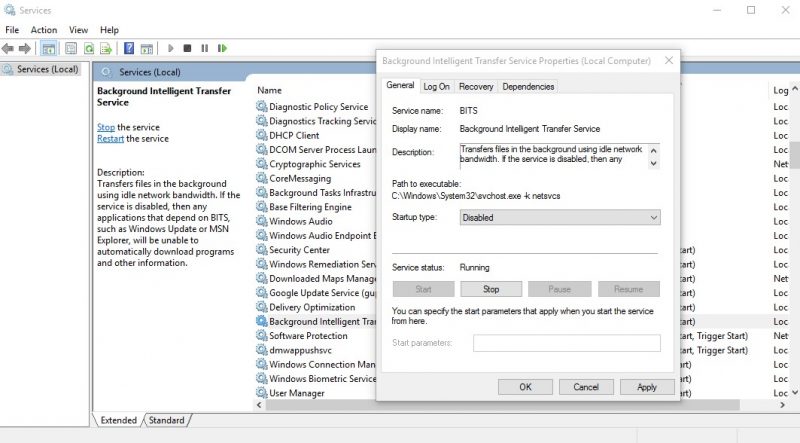
5. Now, find the Intelligent Background Transfer Service (Background Intelligent Transfer Service) among the services. Right-click on it and select Properties. In Startup type, select Disable and click on Apply.
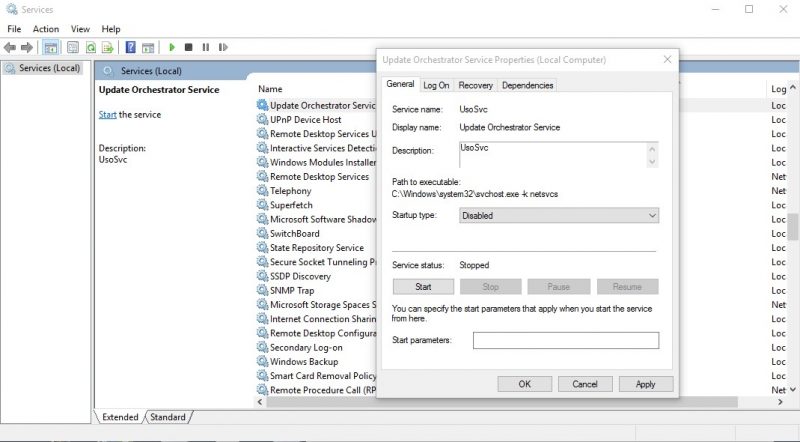
6. In the next step, find the Update Orchestrator Service (Update Orchestrator Service) among the services. Right-click on it and select Properties. Now, in the startup type, select Disable and click on Apply.
2. Disable Superfetch using Command Prompt
If you don't want to follow all the steps mentioned, you can use the Windows 10 command prompt to disable Superfetch. Follow the simple steps below to disable Superfetch using the command prompt.
1. First, right click on the button Windows Start and select the Command Prompt option (Admin).
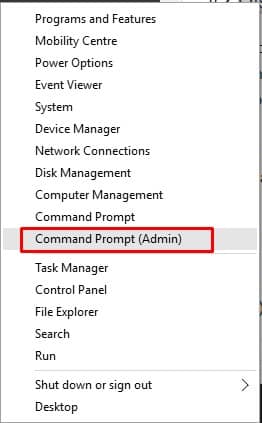
2. Now, you will see the command prompt interface with administrator privileges.

3. Now, in the command prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
net.exe stop superfetch

4. Next, write sc config sysmain start=disabled and press Enter.

3. Run System File Checker
The Checker of Archives System Recovery, or SFC, is a utility designed to find and repair corrupted system files. When system files are corrupted, the Host Service: Local System also experiences high disk usage.
Therefore, we need to run the System File Checker utility to find and replace the corrupted files. Here's what you should do.
1. First, click on Windows search and type Command Prompt. Then, right click on the CMD and select Run as administrator.
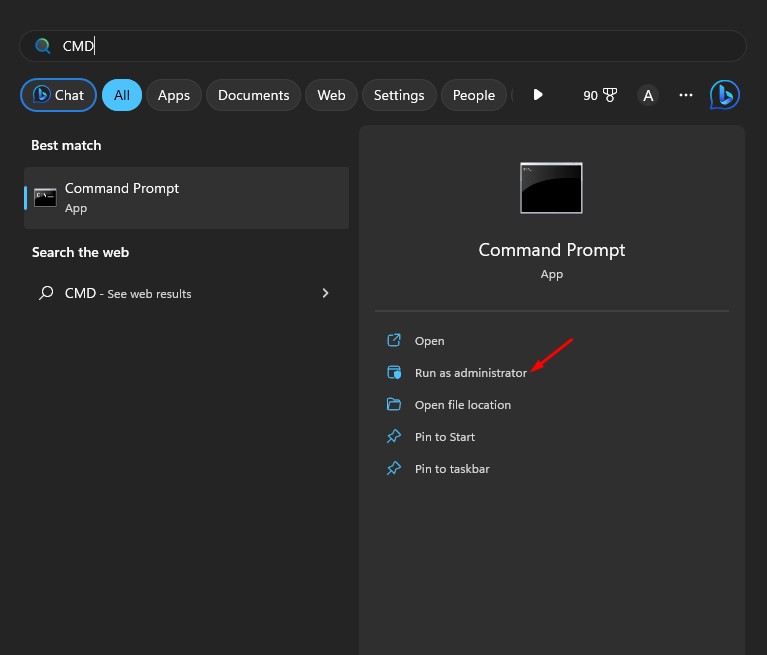
2. When the Command Prompt opens, type the following command and press the Enter button.
sfc /scannow

3. Now, wait until the scan is complete. Once finished, restart your Windows computer.
4. Perform a clean boot
Performing a clean boot is another best way to resolve the issue of high CPU usage of the Host: Local System Service.
A clean boot involves disabling all third-party applications and then restarting your computer. This way, your PC will only run Microsoft services.
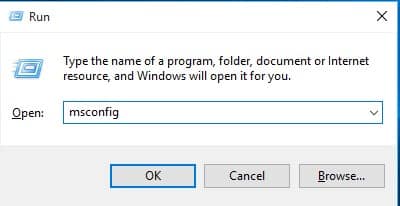
1. Press the Windows key + R on your keyboard. This will open the dialog box Execute. Then write msconfig and press the button Enter.
2. Next, in the System Configuration tab, switch to Services.
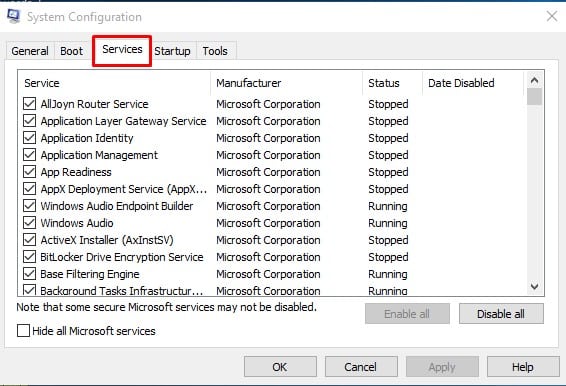
3. Finally, select the option Hide all Microsoft services and click on Disable all.
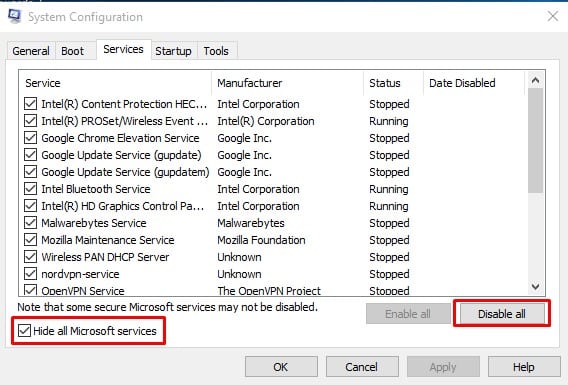
After making the changes, restart your computer. If the problem doesn't occur now, you should enable the services one by one and check which ones are causing the problem.
Here's how to fix the high disk usage of the Host: Local System service on Windows computers. If you have any other questions, be sure to let us know in the comments box below. 💬