Background refresh: Save battery with this trick ⚡
Apple's iPhone has a feature called Background update This allows app content to stay up-to-date, even when you're not actively using the app. 📲
In this guide you will discover how background refresh works on iPhone, its usefulness and how to configure it to optimize your experience.
What is background app refresh on iPhone?
The Background update It's a feature that allows apps to automatically refresh their data, keeping the information up-to-date even when you're not using them. For example, the Mail app on your iPhone always shows new emails without you having to open it manually.
Additionally, on iOS you can manage this feature, turning it on or off completely or only for certain apps as you prefer.
How to enable or disable background refresh on iPhone
Apple gives you the freedom to choose whether you want this feature enabled or not. Follow these steps to customize it on your device:
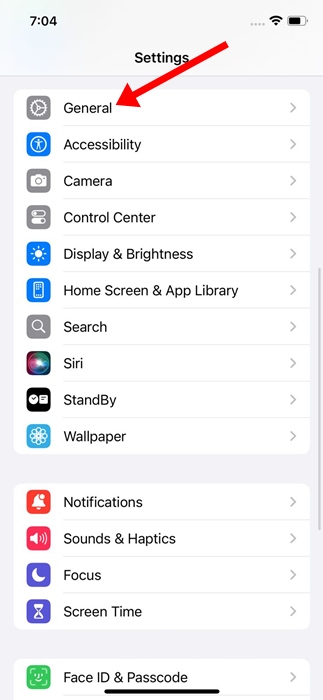
1. Open the app Settings on your iPhone.

2. Select General.
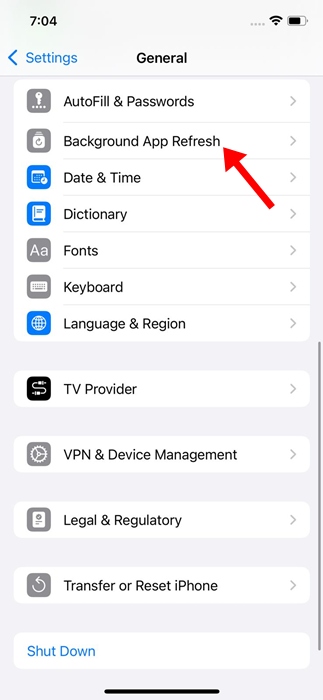
3. Tap on Background update.
4. Press again on Background update.
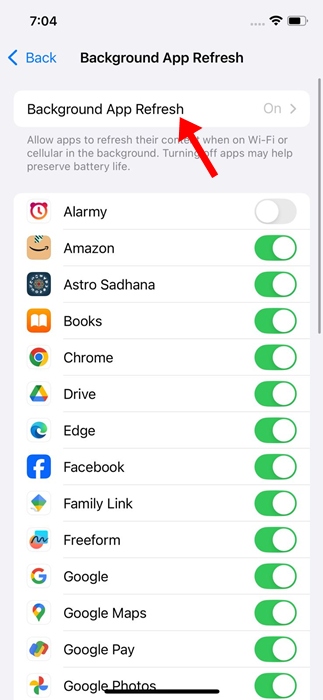
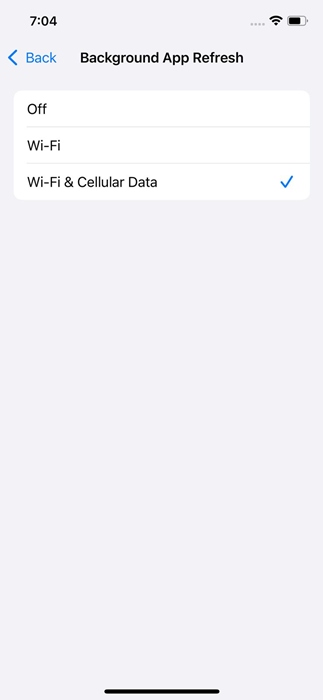
5. Choose one of the three options: WiFi only, WiFi and mobile data (predetermined) the Deactivate fully utilize the function to save battery and data.
How do I manage background updates for specific applications?
If you prefer to control this function app by app, it's very simple:
1. And a Settings > General > Background Refresh.

2. On this screen you will see all the applications installed on your iPhone with a switch next to them.
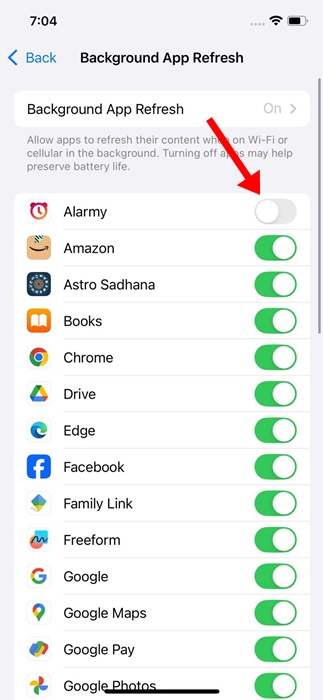
3. Simply turn off the switch next to the apps where you don't want content to update in the background to save battery and data.
Disadvantages of background updates
While this feature makes it easy to keep your apps up to date, it has some drawbacks you should consider:
- It doesn't work if you have the Low power modeto protect the battery.
- On older iPhone models, you may not have the option to choose whether the update is done using Wi-Fi only or also cellular data.
- Constant use may drain the battery faster by keeping apps active in the background.
- It also increases consumption of mobile databecause the apps are constantly connecting to the internet.
Now that you know what background app refresh is and how to set it up, optimize your iPhone to work exactly the way you need it to. Have questions or want to share your experience? Leave us a comment! 💬