Ubuntu won't start? 💻 Discover Quick Solutions 2025.
Over the years, I've encountered a number of different boot issues on Ubuntu, from black screens to endless loading loops. Fortunately, I've discovered several reliable methods to get Ubuntu up and running again. Here's what worked for me. 🚀
The following are not the only possible solutions. Ubuntu's flexibility means that there is often more than one way to solve a problem. problem. Depending on your settings and preferences, one method may work better than another. If you get stuck, the key is keep Curiosity, experimentation and relying on community resources. 🤔
Using Recovery Mode to Troubleshoot Boot Issues
I've had times when Ubuntu simply refused to start—sometimes staying at a black screen, others eternally loading. However, if you can access the GRUB menu, you're in luck! Simply hold down the Shift key o Esc justo después de que desaparezca el logo de BIOS/UEFI (no te sorprendas si te toma un par de intentos acertar en el momento). Una vez que aparezca GRUB, selecciona «Advanced options for Ubuntu” and then choose one of the Recovery Mode entries.
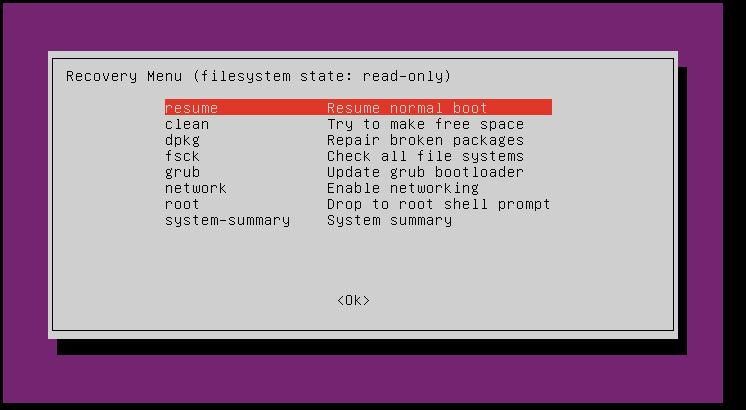
I have found the following two options to be most helpful for common boot problems:
- clean: This attempts free up disk space, which can sometimes prevent Ubuntu from booting if your drive is too full. 🗑️
- dpkg: This attempts to repair corrupted software packages, which can cause boot problems.
Use the keys arrow keys to navigate the menu and press Enter to select an option. It is a good idea to try first clean and then dpkg. After each operation, try to restart the system by selecting resumeIf these options do not resolve the issue, proceed to use the Boot-Repair tool as described below. 🛠️
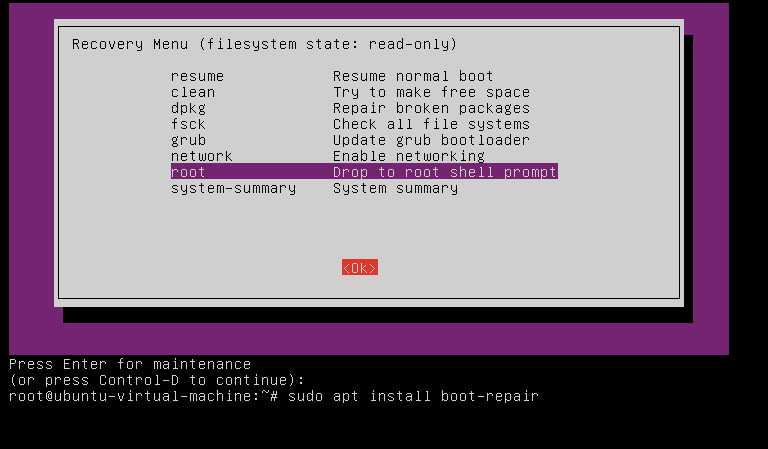
In the recovery mode menu, navigate to root and press Enter. In the terminal that appears, type:
sudo apt install boot-repair
boot-repairIf you see “The boot-repair package cannot be located”, it means that Boot-Repair is not in the boot sources. default software of your system. You need to add a Personal Package Archive (PPA) containing Boot-Repair. In the terminal, type:
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:yannubuntu/boot-repair
sudo apt update
sudo apt install boot-repairNow, run Boot-Repair by typing boot-repair in the terminal. Follow the on-screen instructions. 💻
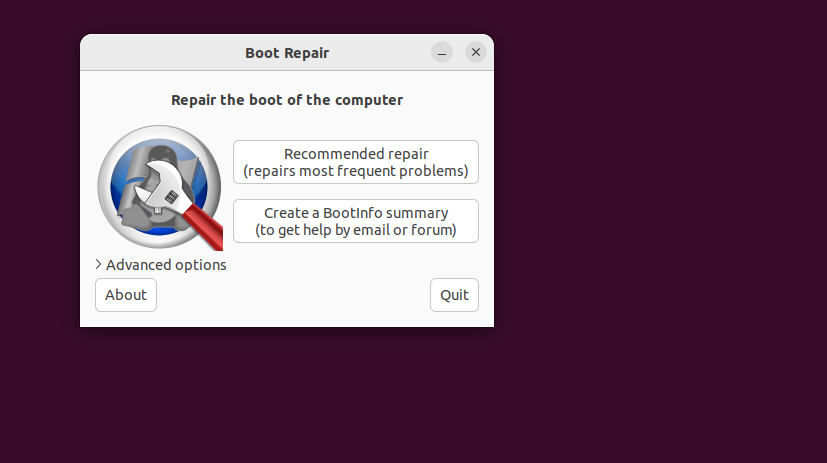
Still Stuck? Use Logs to Find the Problem
If the other steps don't work, you can check the system logs for clues—I've had to do this when nothing else seemed to fix the problem. From the root terminal in Recovery Mode, I ran:
journalctl -xb
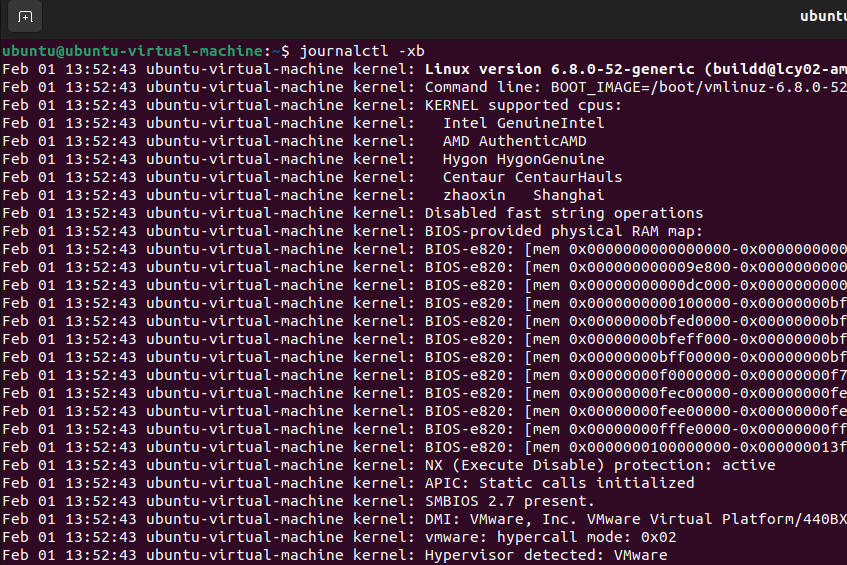
This command allowed me to examine logs detailed boot, discovering a corrupted package as the culprit behind my failure to boot Ubuntu. I then used dpkg in Recovery Mode to repair the package, solving the problem. ✅
Another useful command is:
sudo dmesg | tail -50
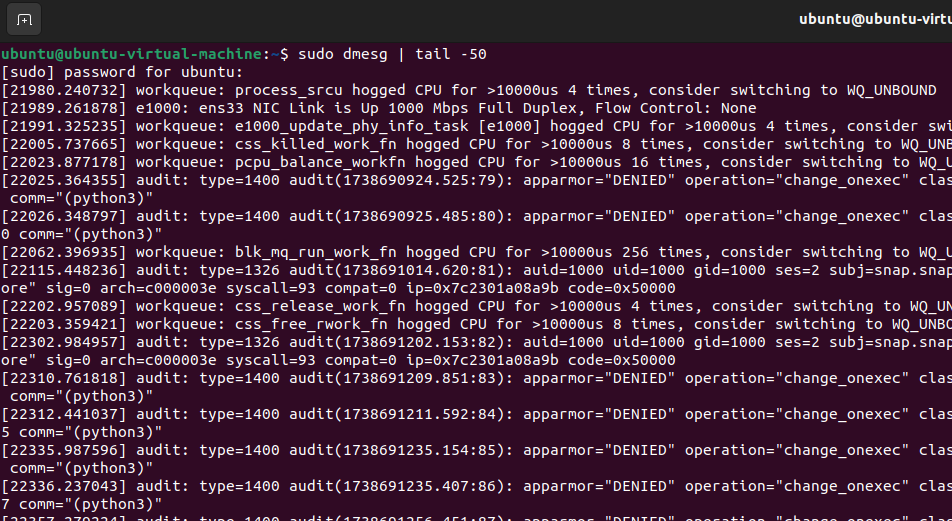
This displays the most recent system messages, which can be useful for detecting Driver failures or hardware problems. If you are stuck and you are not sure of what's wrong, logs like these can give you a better idea of what you need to fix. 🔍
If you can't access GRUB at all, you'll need to use a live USB/DVD.
Use another one computer to create a bootable Ubuntu USB drive. You can download the Ubuntu ISO from the official Ubuntu website and use a tool like Rufus (on Windows) or Boot Disk Creator (on Ubuntu) to create the bootable USB. 💾
Start your computer from the live USB. Open a terminal. Follow the Boot-Repair installation instructions above (including adding the PPA). Then, run boot-repair. This process allows Boot-Repair to access and repair your system's bootloader. Ubuntu installed.
Facing boot problems in Ubuntu can be frustrating, but there is almost always a way to fix them. Whether it's using Recovery Mode, running Boot-Repair, or checking the system logs, the right approach depends on what's causing the problem. In my experience, the key is to stay patient, try different solutions, and use the tools Ubuntu provides. And if all else fails, the Ubuntu community It is a great resource for solving deeper problems. 🤗