Git vs GitHub: Discover the truth in 3 steps 🚀
Key Summary
- GitHub is a platform for hosting and sharing code, offering free web hosting and social features.
- Git is a version control system that tracks code changes and is the technological foundation of GitHub.
- There are other Git hosts such as GitLab and Bitbucket, but GitHub is the most widely used and recognized worldwide.
GitHub is so popular that it's often confused with Git, but they are different concepts. There are alternatives for both, although none are as widespread as GitHub.
What Is GitHub?
GitHub is a web application for developers to host, share, and collaborate on software projects. Many projects are open source and allow public contributions. GitHub fosters community with user accounts, pull requests for change tracking, issue tracking, and wikis for documentation.
Launched in 2008 and acquired by Microsoft in 2018, GitHub has become the primary home for many popular projects. Its GitHub Pages feature offers free web hosting for projects, allowing for a fully-content site on the platform. Additionally, it's possible to edit directly on GitHub or clone repositories to work locally.
GitHub uses Git as the base technology for tracking changes in projects.
What Is Git?
Git is a distributed version control system (VCS) created in 2005 by Linus Torvalds, developer of the Linux kernel. It is free software that records code changes over time, storing differences between versions for unlimited versions. A Git repository is an organized collection of a project's files.
Programmers often use Git on the command line with the command git, which offers many options and subcommands for managing low-level repositories.
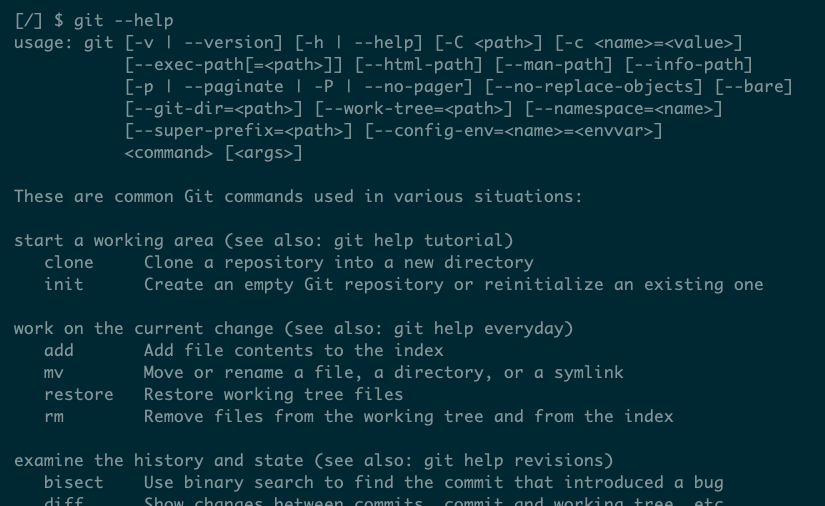
For example, to convert a normal folder into a Git repository you use:
git initThe usual flow involves editing files and then using commands to save versions:
git add file.c git commit -m "Fixed a bug in the checkout process"You can clone a GitHub project, work locally, and push changes to the remote repository. This process works the same with any Git repository, whether on GitHub or other local services or servers.
If the command line is not your thing, there are Git clients with a graphical interface, for example
Other popular clients are Fork, Sourcetree and GitKrakenYou can try several to find the one you like best.
Should You Use a Graphical Git Client?
Git can be complicated for beginners.
Do I Have to Use Both—Or Just One?
You can download software from GitHub without creating an account. Most projects offer executable files in the Releases section, or you can clone public repositories to get the complete code.
If you want to keep a project open to the public, GitHub is ideal for hosting it, but there are also options like GitLab and Bitbucket that offer similar features.
Since everyone uses Git, moving repositories or using multiple hosts is easy. However, GitHub-exclusive features, such as issue tracking or wikis, are tied to the platform. To avoid lock-in, you can limit the use of these features.
GitHub offers a robust API for accessing your data. For example, you can export issues and wikis (which are Git repositories) to migrate to other platforms if you wish.
What is an API and How Do Developers Use It?
You've probably heard of 'API'.
If you are looking for another version control system, Beanstalk supports Git and also Subversion (SVN).
There are other alternatives to Git, such as Mercurial, although they are less popular and recommended only for very specific cases. For most new projects, Git is the best option, and GitHub's integration with Git makes it much easier to use.