AMD Ryzen 9 6900HX – Performance Test
AMD Ryzen 9 6900HX – BenchMark
Ryzen 9 6900HX is among the new processors created by AMD under its new generation of APUs, codenamed 'Rembrandt'.
The series is aimed at the laptop and convertible market and will be available from February.
While the future of the processors As AMD goes through the new ZEN 4 generation, AMD created a product line in the form of a transition.
They use an advanced revision of the ZEN 3+ architecture, are manufactured in processes technological 6nm and will replace the current Ryzen 5000 'Cezanne'.
Apart from increasing performance, AMD takes advantage of the opportunity to sustain the new generation of memoirs DDR5 and its version for LPDDR5 laptops, as well as the latest connectivity standards, Wi-Fi 6E, Bluetooth 5.2 and the latest version of the USB4 peripheral port.
Another aspect highlighted comes from the optimization from the graphics section with the 'Navi2' chips, which use RDNA 2 technology to progress to the veteran 'Vega'.
As for the rest, they are manufactured under an APU (accelerated processing unit) format that adds a central processing unit, GPU, supervisor of memory and other chipset elements in the same package to gain integration, lower consumption and reduce costs.
Ryzen 9 6900HX, performance
In his presentation at the CES 2022, AMD talked about a performance increase double-digit development and even more in the graphics section.
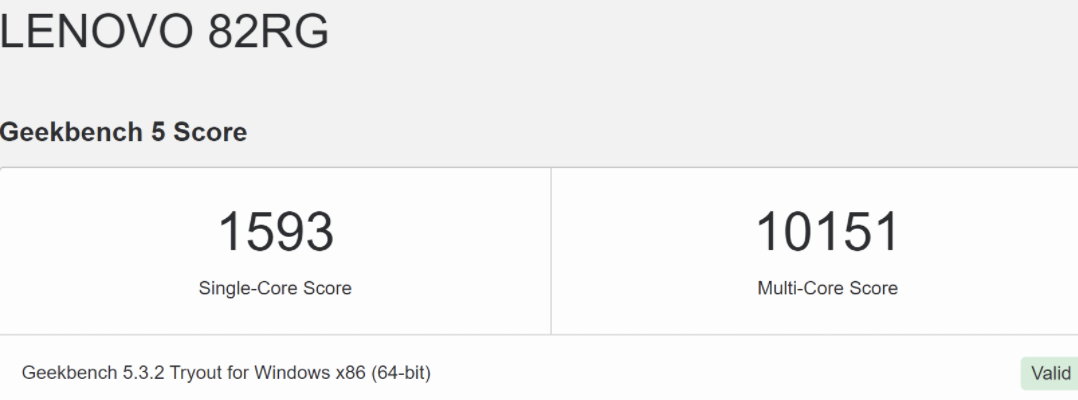
At this moment, from Geekbench We have received the first data from others, specifically about a Lenovo laptop with the Windows 11 operating system.

He Ryzen The 9 6900HX is one of the most attractive models of the ten 'Rembrandt' APUs that AMD will market.
Although it will have 2 other processors on top of it, it is an advance with 8 cores and 16 processing threads with working frequencies from 3.3 to 4.9 GHz.
Its multiplier is unlocked for a TDP of 45 watts, the maximum capacity level of which will be established by each developer depending on the positioning they want for the equipment where they install it and the cooling system they use.
In such a case, Geekbench does not establish it, although it does provide benchmarks that can give us an idea of its performance.
This central processing unit achieves 1593 points in the single-core test and 10151 points in the multi-core test.
This means an increase in 12% and the 33% respectively as opposed to the Ryzen 9 5900HX powered by Zen3 'Cezanne' silicon.
Worse news comes if we compare it with the true rivalry which is none other than the new Intel Alder Lake.
The APU of AMD It is quite below the scores of the Core i9-12900H (From 7 to 21% in single thread and from 37 to 42% in multicore).
Hay que decir que no se conoce la continuidad máxima usada por el Ryzen 9 6900HX para estas pruebas y que requerimos otras alén de test sintéticos para revisar su desempeño real.
In addition to this, the central unit of Intel processing It has many more cores (14) and threads (20) and its price will also be higher.
Where does this leave us? Somewhere in the middle.
There is no doubt that these 6000 series APUs are efficient developments and a optimization essential compared to the previous ones, especially in the graphics section with the new RDNA 2 chips.
Another thing will be to challenge Intel.
The huge one chip AMD did a great job with Alder Lake and AMD may not be able to compete in performance until its next ZEN 4 architecture arrives.
Of course, we still need to understand cost setting and how it affects the final cost of the products. laptops and convertibles where they will be installed.
There is plenty there for AMD to convince OEMs.
We will understand soon.
We expect launch next month.
In case you didn't see it at the time, we leave you with the official catalogue of these 'Rembrandt' APUs.
AMD Ryzen 6000 Series
| Model | Cores/Threads | Max continuity | Cache | TDP |
| Ryzen 9 6980HX | 8 / 16 | Up to 5.0 GHz | 20 MB | 45W+ |
| Ryzen 9 6980HS | 8 / 16 | Up to 5.0GHz | 20 MB | 35W |
| Ryzen 9 6900HX | 8 / 16 | Up to 4.9GHz | 20 MB | 45W+ |
| Ryzen 9 6900HS | 8 / 16 | Up to 4.9GHz | 20 MB | 35W |
| Ryzen 7 6800H | 8 / 16 | Up to 4.7GHz | 20 MB | 45W |
| Ryzen 7 6800HS | 8 / 16 | Up to 4.7GHz | 20 MB | 35W |
| Ryzen 7 6800U | 8 / 16 | Up to 4.7GHz | 20 MB | 15-28W |
| Ryzen 5 6600H | 6 / 12 | Up to 4.5GHz | 19 MB | 45W |
| Ryzen 5 6600HS | 6 / 12 | Up to 4.5GHz | 19 MB | 35W |
| Ryzen 5 6600U | 6 / 12 | Up to 4.5GHz | 19 MB | 15-28W |