ADB Commands: 9 Android Tricks You Should Know Now ⚡📱
ADB, or Android Debug Bridge, is a powerful tool that lets you control your Android device from a computer. Whether managing apps, capturing screenshots, or accessing system logs, ADB simplifies tasks and unlocks advanced features, making it a must-have for every Android user. 🚀
What is ADB and why use it?
ADB, or Android Debug Bridge, is a command-line tool that allows you to control your Android device beyond the standard settings. By entering commands in the terminal from your computer, you can communicate directly with your device and unlock advanced features, as well as perform tasks that are not available through regular menus.
Acting as a bridge between your device and your computer, ADB It lets you install apps, transfer files, capture screenshots, access system logs, and much more. It's a powerful tool for anyone looking to customize, troubleshoot, or improve their Android experience. 💻📱
Why use ADB? It simplifies tasks like debugging apps, checking connectivity, or troubleshooting system issues, making them faster and easier. Whether you're a developer or a tech-savvy user, ADB opens up a world of possibilities for taking full control of your device. Android. 🌟
Getting started with ADB
Getting started with ADB is easy. First, download and install the Android SDK Platform-Tools on your computer. Next, enable developer options on your Android device by tapping "Build Number" in Settings, followed by enabling "USB Debugging." Then, connect your device to your computer via USB, authorize the connection, and you're all set! For more detailed instructions, check out this article on how to install ADB. 📥
If you prefer a wireless setup, you can connect your device to your computer over Wi-Fi after an initial USB connection. Wireless ADB is great for tasks like testing apps or tweaking settings on the fly. For more information on how to set it up, check out this guide on how to enable wireless ADB. 📶
9 ADB Commands Every Android User Should Know
Once you've set up ADB, it's time to explore the commands that make it so powerful. ADB commands are designed to simplify tasks, improve efficiency, and unlock advanced features on your Android device. Here are nine essential commands every Android user should know—don't worry, they're easy to use! 🙌
Check Device Connectivity
Command:
adb devices
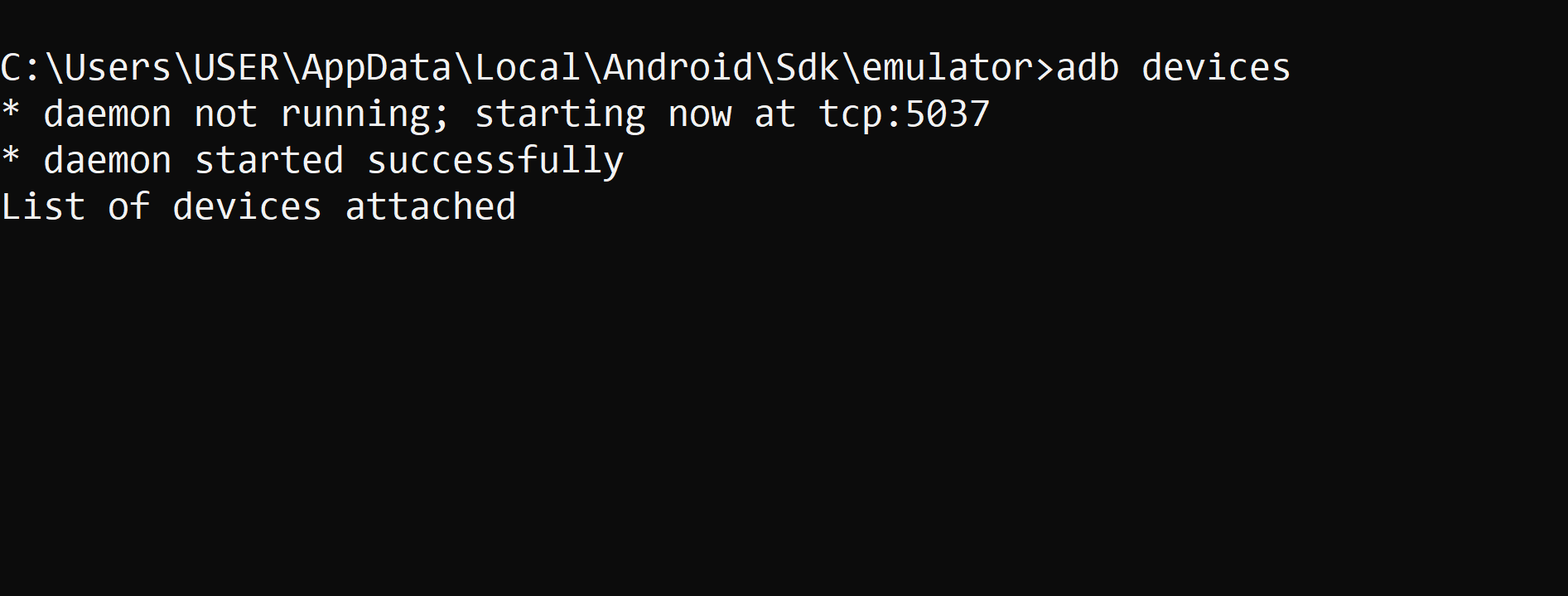
Run this command in your terminal or command line to verify that your Android device is properly connected to your computer. This command lists all devices connected to your system, ensuring ADB is ready for use. 🔌
If your device isn't connected, the command will return an empty list, indicating that ADB can't detect devices. 🚫
However, if the connection is successful, you'll see a list of connected devices. For example:
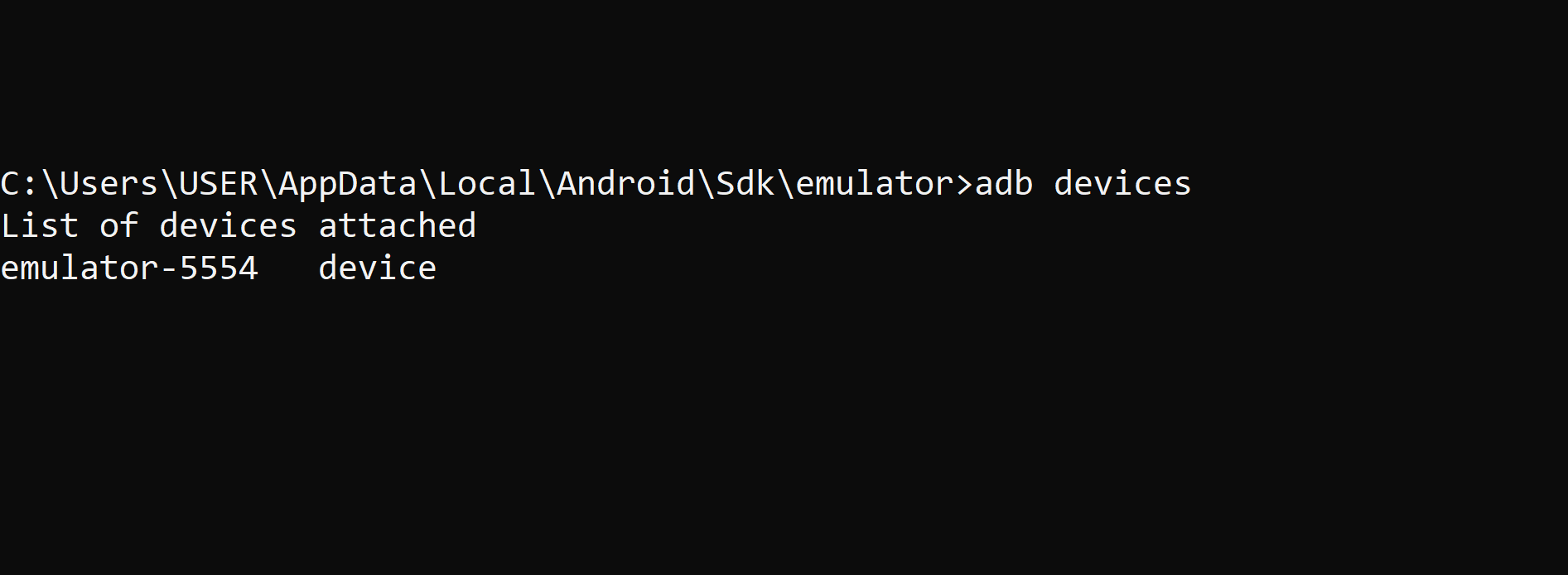
This quick check ensures ADB is ready to use before you start running other commands. If your device doesn't appear, check your USB connection again, make sure USB Debugging is enabled, and, if prompted, authorize the connection on your device. 🔍
Install an Application
Command:
adb install
This command allows you to quickly install APK files on your Android device without the hassle of navigating through menus. You only need the path to the APK file on your computer. 📦
For example, to install the Twitter Lite APK, you would run:
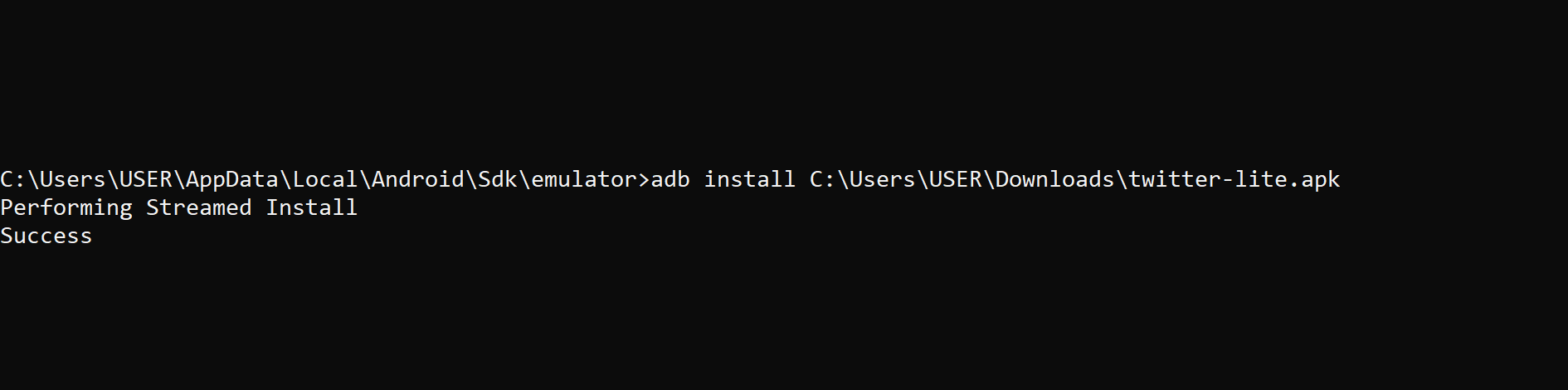
Once the installation is complete, the app will appear on your phone, ready to use. This is especially useful when testing apps or installing APKs that aren't available on the Google Play Store. 📲
If you encounter any issues, check the file path and make sure your device is properly connected.
List Installed Applications
Command:
adb shell pm list packages
This command gives you a complete list of all the apps installed on your Android device, showing their package names. It's particularly useful when you need to identify apps for management tasks like uninstalling or wiping data. 🗂️
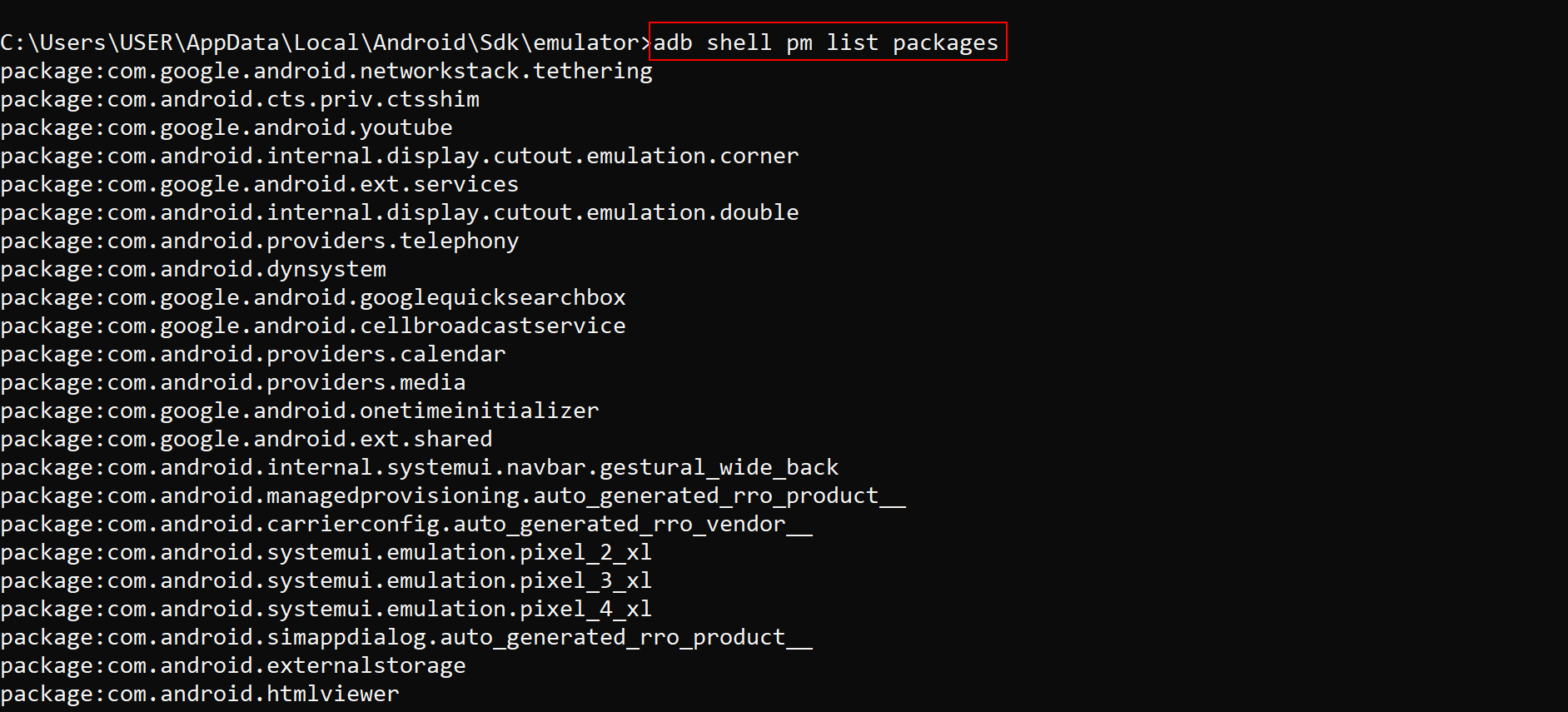
Since the full list can be overwhelming, you can search for specific applications or packages to save time. Use the following commands depending on your operating system:
On Windows: Use the findstr command
adb shell pm list packages | findstr twitter
On Linux or macOS: Use the grep command
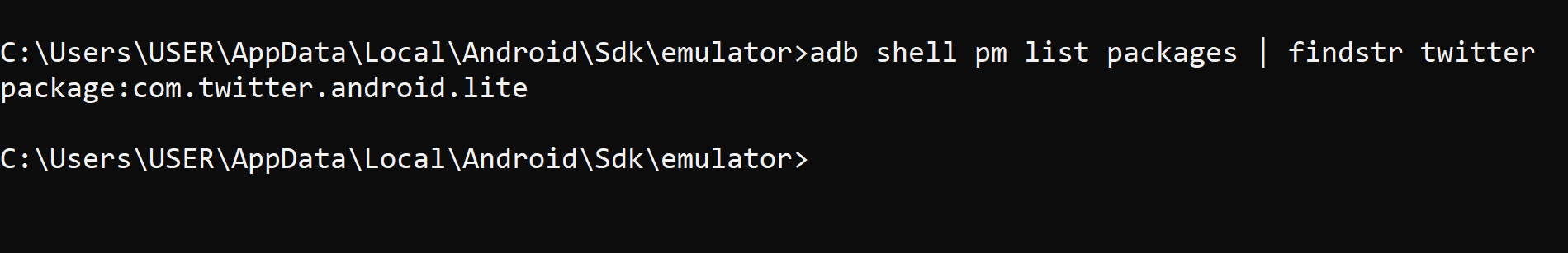
adb shell pm list packages | grep twitter
For example, searching for “Twitter” will return:
Uninstall an Application
Command:
adb uninstall
This command removes unwanted apps from your device by specifying their package name. It's a great way to remove bloatware, free up space, or uninstall apps you're testing. 🗑️
First, make sure you have the correct package name for the app you want to uninstall. For example, to uninstall Twitter Lite, you may have identified its package name earlier as:
com.twitter.android.lite
So, you would run the command:
adb uninstall com.twitter.android.lite
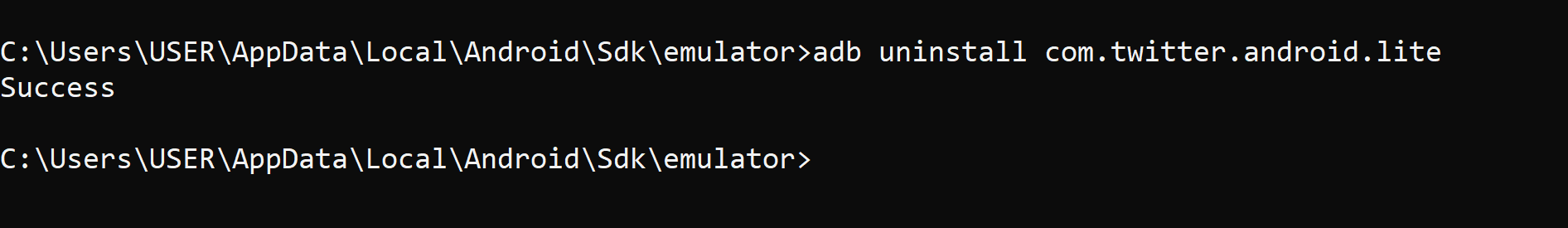
Twitter has been uninstalled. ✔️
Take a Screenshot
Command:
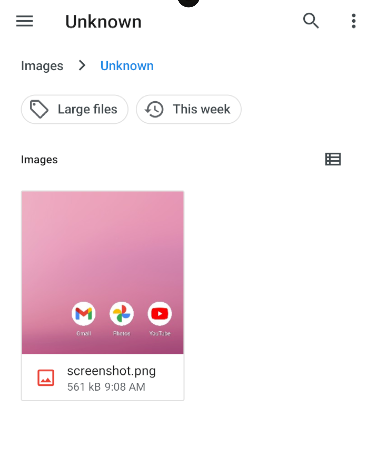
adb shell screencap /sdcard/screenshot.png
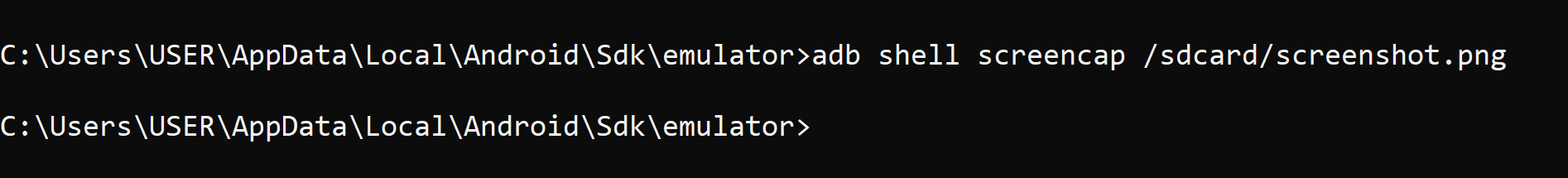
This command captures your device's screen and saves it to your phone's storage, specifically the /sdcard directory. It's perfect for situations where you need to take a snapshot without using any physical buttons. 📷
Record Your Screen
Command:
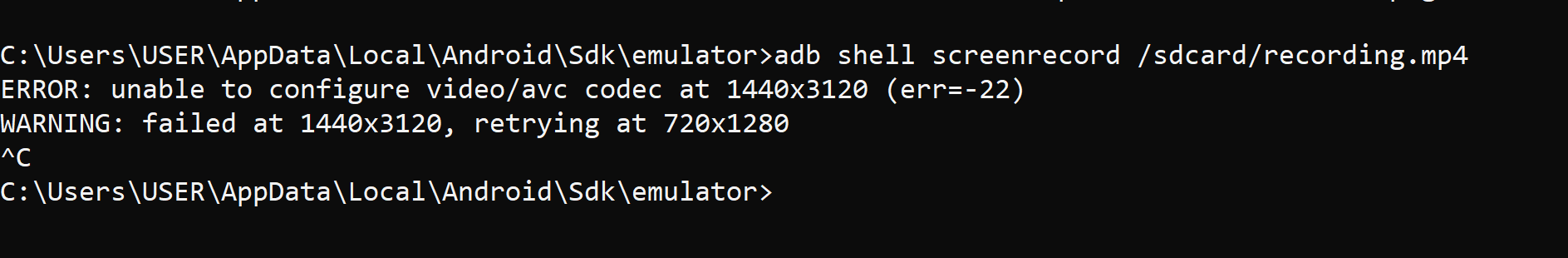
adb shell screenrecord /sdcard/recording.mp4
With this command, you can record everything that happens on your Android device's screen and save it as a video file. It's ideal for creating tutorials, showcasing app features, or sharing gameplay footage. 🎥
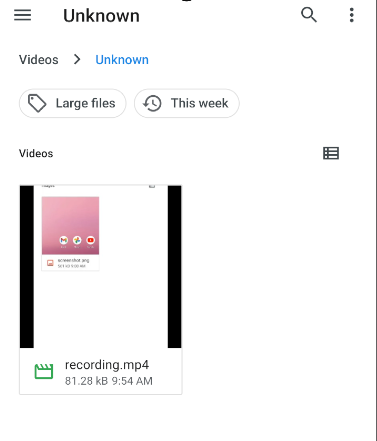
Recording will start immediately and will be saved to your device's /sdcard directory as recording.mp4.
To stop recording, press Ctrl + C on the terminal or let the recording stop automatically after 3 minutes (default duration). ⏳
Manage Files
With ADB, transferring files between your computer and Android device is a breeze. These commands are perfect for backing up data, transferring media, or sending configuration files to your device. 📂
Commands:
adb push
Transfer files from your computer to your device.
adb pull
Copy files from your device to your computer.
Access System Logs
Command
adb logcat
This command allows you to view detailed logs from your Android device in real time. It's an invaluable tool for developers debugging apps, and can also help identify issues or track down bugs in your device's performance. 📊
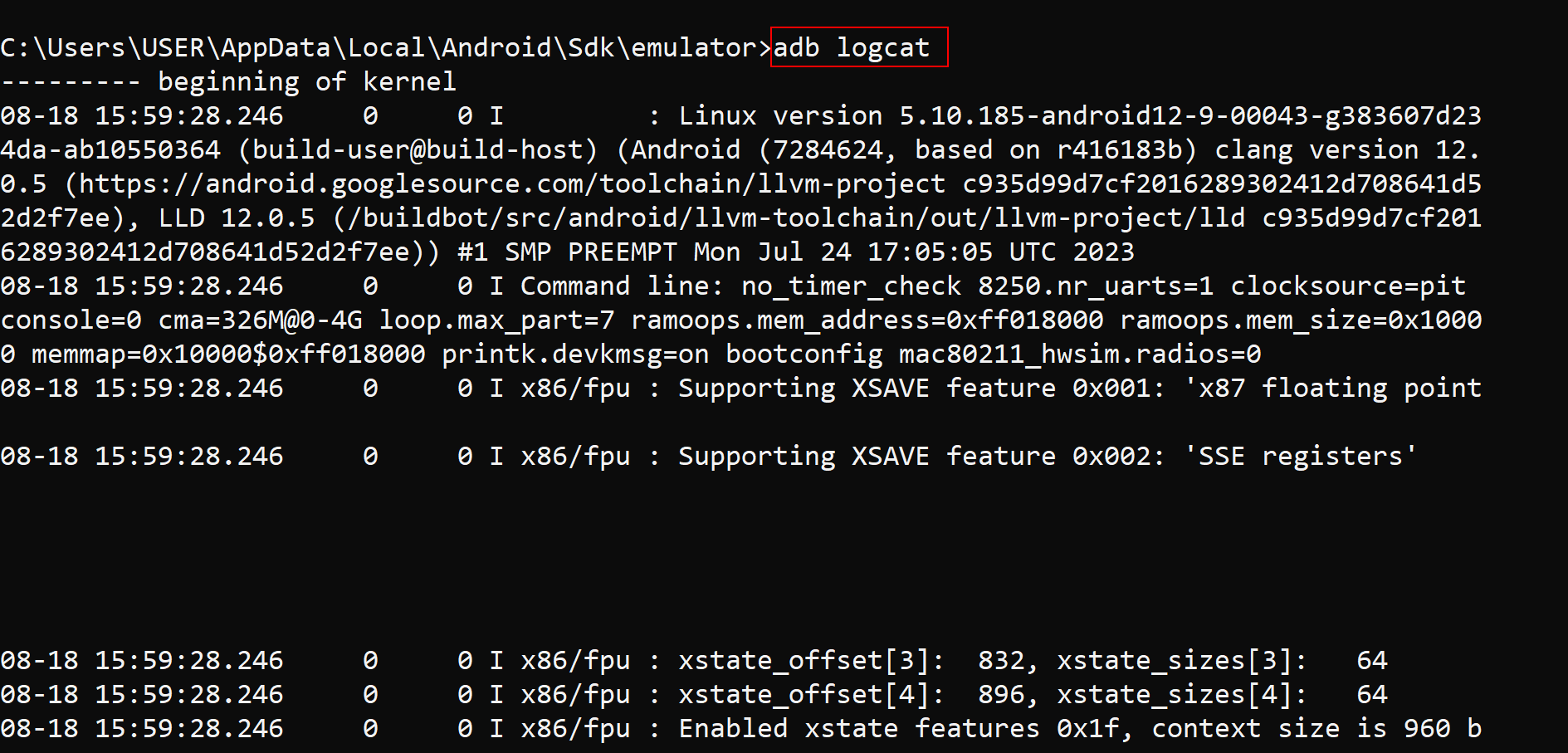
Your terminal will display a live feed of system logs, including application activity, system messages, and error reports.
Restart your Device
Command:
adb reboot
Rebooting your Android device is as simple as running this command, eliminating the need to manually press the power button. If your phone is unresponsive or you're in the middle of debugging, you can easily reboot with this command. ♻️
Tips for Safely Managing ADB
ADB is a versatile tool, but caution is key. Connect only to trusted computers, avoid enabling USB debugging in public and always double-check commands to prevent accidental changes. And always verify file paths and package names to avoid data loss or system issues. 🔒