How to Remove Chrome Extensions ❌ Easy 3-Step Solution
Are you trying to remove a Chrome extension and notice that the button Eliminate Is it disabled or just not showing up? 😤 This problem can be frustrating, but it's crucial to act quickly to avoid risks like browser hijacking, malicious file installation, or invasive adware.
When you can't uninstall a Chrome extension, it's a sign of a serious problem that requires immediate attention to protect your privacy and digital security.
Why can't I uninstall some Chrome extensions?
There are several reasons why you might not be able to remove certain Chrome extensions. Here are the most common reasons why uninstallation is blocked:
- Your browser is managed by an organization (a company or educational institution).
- Incorrect Chrome policy settings.
- Browser hijacking.
- Presence of adware that prevents removal.
- Use of a outdated version of Chrome.
To remove those stubborn extensions, follow these recommended steps to diagnose and resolve the problem, even if you don't know the exact cause yet.
1. Check if Chrome is managed by an organization
If you use Chrome on a work or school computer, you might see the message “Your browser is managed by an organization”.
This indicates that browser policies are controlled by that organization and you won't be able to uninstall extensions or modify certain settings.

If you see that message on your personal computer for no apparent reason, it is likely that you browser has been hijacked by malware.
This hijacking is often accompanied by other symptoms such as excessive unwanted ads, slowness, or persistent browser crashes.
2. Run the Chrome Policy Remover script
Stefan VD, a recognized Chrome expert, developed a script called Chrome Policy Remover that eliminates malicious policy settings and hard-to-remove extensions.
This script is effective for eliminate extensions that display intrusive ads or block uninstallation from Chrome.

Visit this official website to download the script and run it as an administrator on Windows. When prompted for permissions, confirm to continue.
Upon completion, the message will appear “All Chrome Policies are removed”, indicating that the malicious configurations were removed.
On Mac, to run the script you will need to allow it from Settings > Privacy & Security > Open Anyway to prevent GateKeeper from blocking it.
3. Scan your PC with Malwarebytes
Malwarebytes is an advanced security tool that detects and removes malware, adware, and potentially unwanted programs (PUPs).
It is much more effective than Windows' default security at combating browser hijackings and hidden threats.

You just have to download and install Malwarebytes, run a full scan and in just a few minutes it will identify and remove suspicious files that are blocking extensions.
4. Reset the Chrome browser
Use this option only if nothing else works, as resetting Chrome will return your settings to their original state, affecting your home page, pinned tabs, and disabling all extensions.
Steps to reset Chrome:
1. Open Chrome settings.
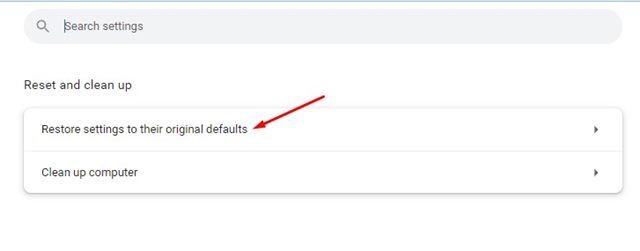
2. In the side menu, select Reset settings.
3. Click on Restore settings to their original default values.
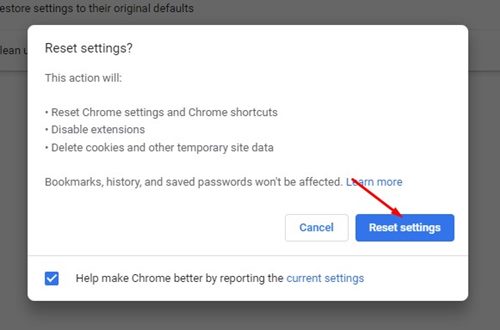
4. Confirm in the pop-up box by clicking on Reset settings.
Then, sign in with your Google account and try uninstalling the problematic extension again.
5. Reinstall the Chrome browser
If the problem persists after resetting Chrome, the best solution is to uninstall and then reinstall Chrome.
This will remove any remaining harmful settings or extensions that could not be removed previously.
Follow these tips and you'll have complete control over your extensions! If you need additional help, leave your questions in the comments 👇 and we'll get back to you quickly.