AMD Introduces Industry’s First Ultra Ethernet-Ready Network Card for AI and HPC
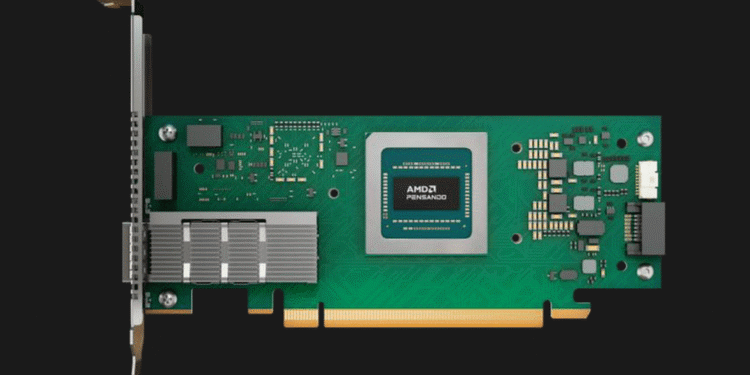
The Ultra Ethernet Consortium (UEC) has delayed the release of version 1.0 of the specification from Q3 2024 to Q1 2025, but it appears that AMD is ready to announce a true network interface card for AI data centers that is ready to be deployed in Ultra Ethernet data centers. The new unit is the AMD Pensando Pollara 400, which promises up to a six-fold performance increase for AI workloads.
The AMD Pensando Pollara 400 is a 400GbE Ultra Ethernet card based on a processor designed by the company's Pensando unit. The network processor features a programmable hardware pipeline, programmable RDMA transport, programmable congestion control, and communications library acceleration. The NIC will be sampled in the fourth quarter and will be commercially available in the first half of 2025, just after the AMD Pensando Consortium Ultra Ethernet formally publish the UEC 1.0 specification.
The AMD Pensando Pollara 400 AI NIC is designed for optimize AI and HPC networks through several advanced capabilities. One of its key features is intelligent multipathing, which dynamically distributes data packets across optimal paths, avoiding network congestion. red and improving overall efficiency. The NIC also includes control path-aware congestion control, which redirects data away from temporarily congested paths to ensure a continuous flow of high-speed data.
 (Image credit: AMD)
(Image credit: AMD)
Pollara 400 is an innovative solution that offers fast failover, which means it can detect and avoid network failures very quickly and effectively. This ensures that communication between graphics processing units (GPUs) remains uninterrupted, which is crucial for applications requiring high throughput. performance and continuous availability. By ensuring seamless GPU-to-GPU communication, Pollara 400 provides robust performance while optimizing utilization of artificial intelligence (AI) clusters and minimizing latency that could negatively impact the prosecution of data.
These advanced features of Pollara 400 are especially promising, as they have the potential to significantly improve the scalability and reliability of AI infrastructure. This makes the solution ideal for large-scale deployments, where efficiency and continuity of the service are of utmost importance.
In parallel, the growth of the Ultra Ethernet Consortium reflects the interest and expansion in the development of technologies networking. With 97 members, a significant increase compared to the 55 in March 2024, the consortium is working on the UEC 1.0 specification. This specification aims to scale the technology Ethernet, which is ubiquitous, in terms of performance and features, to meet the demands of artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) workloads.
The new UEC 1.0 specification will benefit from the reuse of as many of the components as possible. technology Original Ethernet. This not only ensures the cost-effectiveness of developing and implementing new technologies, but also ensures interoperability with existing infrastructures, which is crucial for smooth market adoption.
Additionally, the UEC 1.0 specification will include distinct profiles for AI and HPC. While these types of workloads share a number of similarities, they also have significant differences in their needs and characteristics. Therefore, to maximize the efficiency of each, separate protocols will be developed that specifically fit the unique requirements of AI and HPC. This will enable organizations to get the most out of their technology infrastructures, optimizing performance and ensuring that the workloads are supported. solutions are suitable for a wide range of applications and scenarios.