Windows 11 Native Sandbox
Windows 11 Native Sandbox
Windows 11's Reserved Space optimizes security
Windows 11 Sandbox, also known as Windows Sandbox, is a security solution that Microsoft introduced in the spring 2019 release of Windows 10 and has maintained ever since.
In case you don't know it, it lets users create a separate environment in the system for evaluate/implement programs or applications of prominent danger with all security or navigate websites with the browser that can be dangerous without harming the system or files where they are executed.
For this, Windows Sandbox creates a temporary desktop environment by installing a super-reduced version of Windows of precisely 100 Mbytes and with a kernel separate and apart from the PC on which it runs.
Apart from the securityMicrosoft touts its effectiveness and availability as virtues since it is designed to be disposable.
That is, when we have finished making the apps or applications and we close this tool, the entire environment generated on the computer's disk will be deleted.
A good way to check the danger of unknown apps or find out which websites are safer security controversial through a function that is considerably easier than using virtual machines, since it does not require downloading ISO images or using hypervisors or third-party apps.
Windows 11 Reserved Space
The feature maintains the minimum requirements established for Windows 10, although you already know that these have increased from general form in Windows 11 with TPM, DirectX 12 and others.
To arrange this environment you need:
- Windows 11 Pro, Enterprise, or Education. (Windows Sandbox doesn't currently work with Home editions.)
- A PC with AMD64 architecture.
- At least 2 central unit cores prosecution (4 cores with hyperthreading are recommended).
- At least 4GB of RAM (8GB recommended).
- At least 1 GB of free space in hard disk (it is recommended to use SSD).
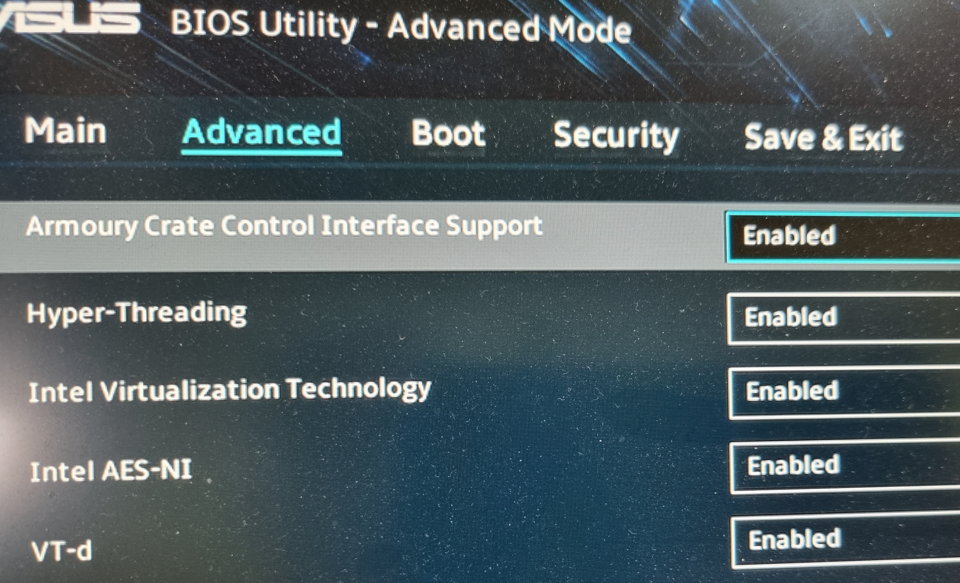
- Virtualization capabilities enabled in BIOS.
Check virtualization capability
Like any other virtual machine, the space set aside from the operating system Windows 11 requires the PC's central processing unit to have virtualization capability enabled.
In processors AMD's virtualization feature is called 'AMD-V' and is enabled by default on supported models which tend to be all of them as of late.
If you use Intel processors, technology virtualization is called 'Intel VT' and is not usually enabled by default.
Activation is done in the BIOS/UEFI as we have seen in the practical article.
Facility
The installation of Windows Sandboxing can be done in a number of ways.
One of them is entering the auxiliary specifications of Windows where you will see this secluded space.
For this:
- Search for “Windows peculiarities”:

- Enables the “Set aside space” box from Windows»:

Another way to turn on the Windows 11 operating system's reserved space is through the Windows 11 window. console advanced Powershell in manager mode, by typing the command Enable-WindowsOptionalFeature -FeatureName “Containers-DisposableClientVM” -All -Online

Either way you will have to restart the device and from there you will now see it installed in the start menu.
Its execution is carried out like all types of apps.
You will see a reduced installation of the operating system Windows 11 where you can install the apps you need, browse the websites you want or copy and paste suspicious files from the host device.

As we stated above, this minimal version is completely separated from the main system and when it is closed Any genre or remainder of file, configuration or work is deleted that you have made.
Every time you run it again you will get a new instance of this reserved space.
Like all OS can be adjusted through simple configuration files, which provide a minimal set of customization factors for the dedicated space, controlling factors such as virtualized GPUs, networking, start commands, audio and video inputs, printer redirection, and others.
What exactly do we use Windows Sandbox for?
The tool has various uses, mainly for browsing potentially dangerous websites and thus evaluating unknown apps.
Some examples:
Contrast apps.
It is not difficult to come across unknown and unreliable apps.
They can be useful, but they can also be dangerous or even contain software malicious.
Windows Sandbox lets you do almost anything that a PC or Mac can do. computer standard by introducing the execution of an antivirus to review these apps.
The global Internet is infested with unsavory sites including those that are engaged in distributing malicious software, advertising content or have fraud schemes. phishing.
If you want to enter a portal Internet suspicious without putting your device at risk, this remote environment leaves it not allowing changes to the real system.
In case of infection or danger, it is simply a matter of closing the session.
Evaluate program.
It is also possible to evaluate any type of program that, although not risky, we do not know or are not familiar with. Insurance to consider preserving it for later.
This environment provides an ideal testing environment, since you can set up and run an app without leaving any trace or residue on the main OS or occupying any elements, memory, storage, or in the Windows registry.
File Checking.
Among the most widely used forms of distribution of software malicious comes from attached files.
For example, in the application by e-mail.
If you want to check email messages and such files, this environment can help.
The same goes for a file with macros or any kind of file that you want to run on your computer.
Even if it has inside software malicious, once you click close in the environment the device will be completely clean of it.
Really useful for the highlighted functionalities this space apart from Windows 11.
Sandbox application on Windows 10 pro operating system.
If you use the operating system Windows 10 or Windows 10 Pro, the good news is that since the spring 2019 version you can have it and use the sandboxie function in the same way, that is, the same features of Windows 11.
Contact us for Windows 10 or 11 installations and configurations.
or by Notebook Repair – Technical Service No. 1





















Thank you so much for sharing. I learned a lot from your article. Great. Thanks.
Thank you so much for your kind comment! I'm glad to hear the article was helpful and that you learned about using the native Sandbox in Windows 11. If you have any questions or would like to delve deeper into any aspect, please don't hesitate to ask. Thanks for following the content!