See CPU temperature Windows 10
What temperature should a processor normally have?
Measuring the CPU temperature on a PC is not difficult.
Today there are many apps that allow us to do it effortlessly, but we do not always know what tests should be performed and how they should be done. interpret the results and which of those results are truly essential.
For example, more than once people have told me that “these results must be wrong, I have exactly the same processor as you and it doesn’t go over 50 degrees.” I have also been told, with a look of astonishment, “my CPU reaches 85 degrees, it can’t be normal, a friend told me it should be at 60 degrees.”
It is necessary to contextualize appropriately.
These kinds of comments affirm that there is still a lot of misinformation about this topic, and that It is a requirement to contextualize appropriately how the different CPU temperature measurement tests were carried out so that, in the end, we can properly interpret the results that were obtained.
Here's an example of what I said before. I asked the person who told me that his CPU doesn't exceed 50 degrees what he was doing when it reached that temperature and he told me that he was playing an arcade game through MAME while listening to music on YouTube.
Yes, it is a complete farce, and I didn't want to go any further, I didn't waste time explaining anything. For reference, as I write this I have YouTube open with my favorite music, Telegram and multiple tabs, Steam and also iCUE and the CPU usage is between 1% and 3%, which causes my temperature to go up. Ryzen 7 5800X is around 36 degrees on average.
From the above you will now have deduced something that I have told you in several analyses, and it happens that the temperature that a component It depends on several factors, but Among the most essential is the workload to which it is subjected.
A processor that is working under minimal load will register a much lower temperature than one that is under much more stress. Hence, it is so essential to measure the temperature of your CPU. computer under different workloads, to have a real and adequately contextualized vision of these values.
Application to measure CPU temperature – PC
How to see my CPU temperature in Windows? How to check the temperature in real time?
As I told you at the beginning of the product, there are currently many reliable apps with which we can measure the CPU temperature.
One of my favorites is AIDA64, which has a fairly complete free version for this purpose, as it can display the temperature of each CPU core and provide an average CORE TEMP (core temperature), which is the value we should take as a reference.
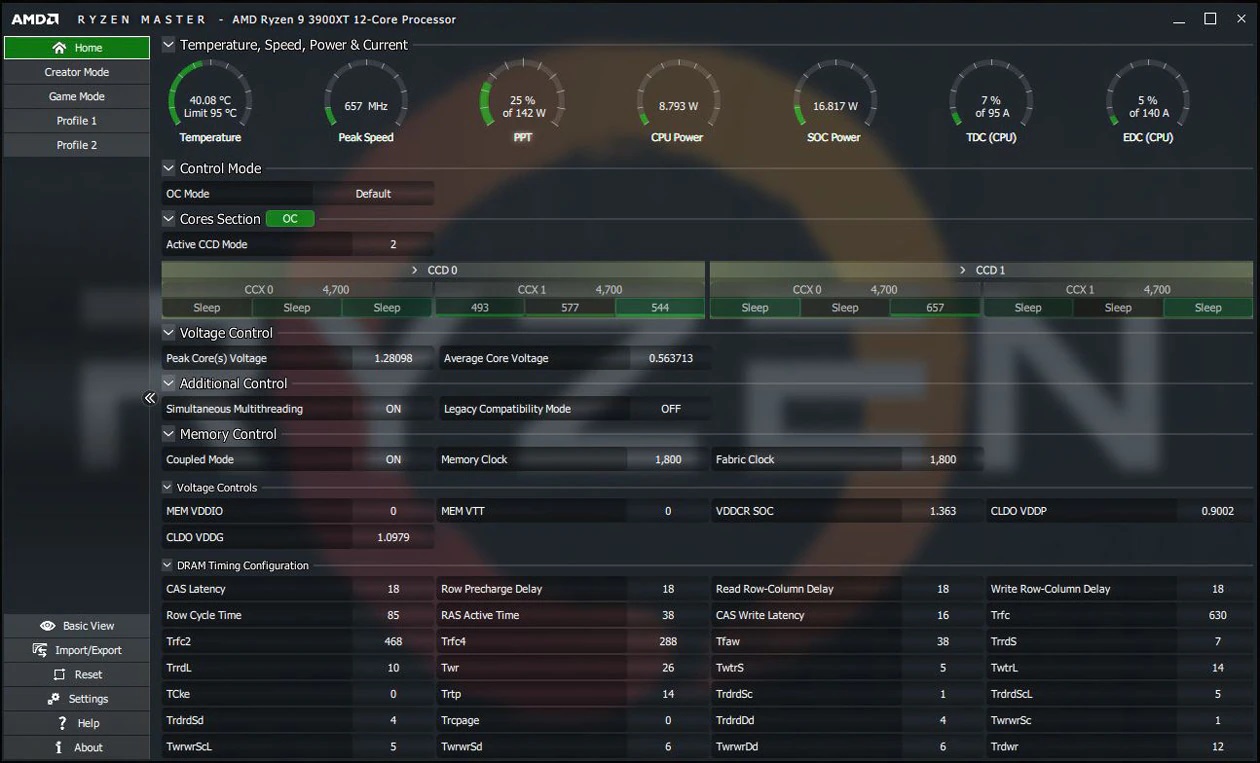
However, to monitor the temperature of your PC on Windows 10 and 11 operating systems, we have the possibility of using apps like Ryzen Master, if we have an AMD central processing unit, or the program Extreme Tuning Utility, if we have an Intel central processing unit.
With both apps we can check the temperature for free, it will allow us to monitor the temperature of our equipment, it has a very easy-to-use interface, with information detailed, on key points of the processor, including the CPU temperature, the workload to which it is subjected and also if any type of "thermal throttling" is being generated, which is nothing more than a loss of performance caused by excess heat.
Some of these apps will help you to correctly measure the temperature of the processor, whether it is a portable or a desktop computer. They are very easy to use, since you don't have to go into complex configurations, you just have to download, install and launch them. However, if you have any questions, you can leave them in the comments and I will help you resolve them.
View CPU temperature Windows 10 – Tips to know the CPU temperature on your Windows 10 and 11 PC
The first thing you need to be clear about is the specification of your CPU based on three key factors that I will explain to you now:
- Does it work at the manufacturer's standard frequencies or is it overclocked? Overclocking can increase performance, but it increases power consumption and temperatures.
- Does it use a top-of-the-range cooling system or something more affordable? The dissipation system can make a very big difference, to control the temperature, while a fan A 65 watt fader is not going to do the same job as one with a 150 watt fader capacity.
- Do you have the power limiter enabled? This affects the maximum CPU consumption. It may improve performance, but it will also increase normal working temperatures.
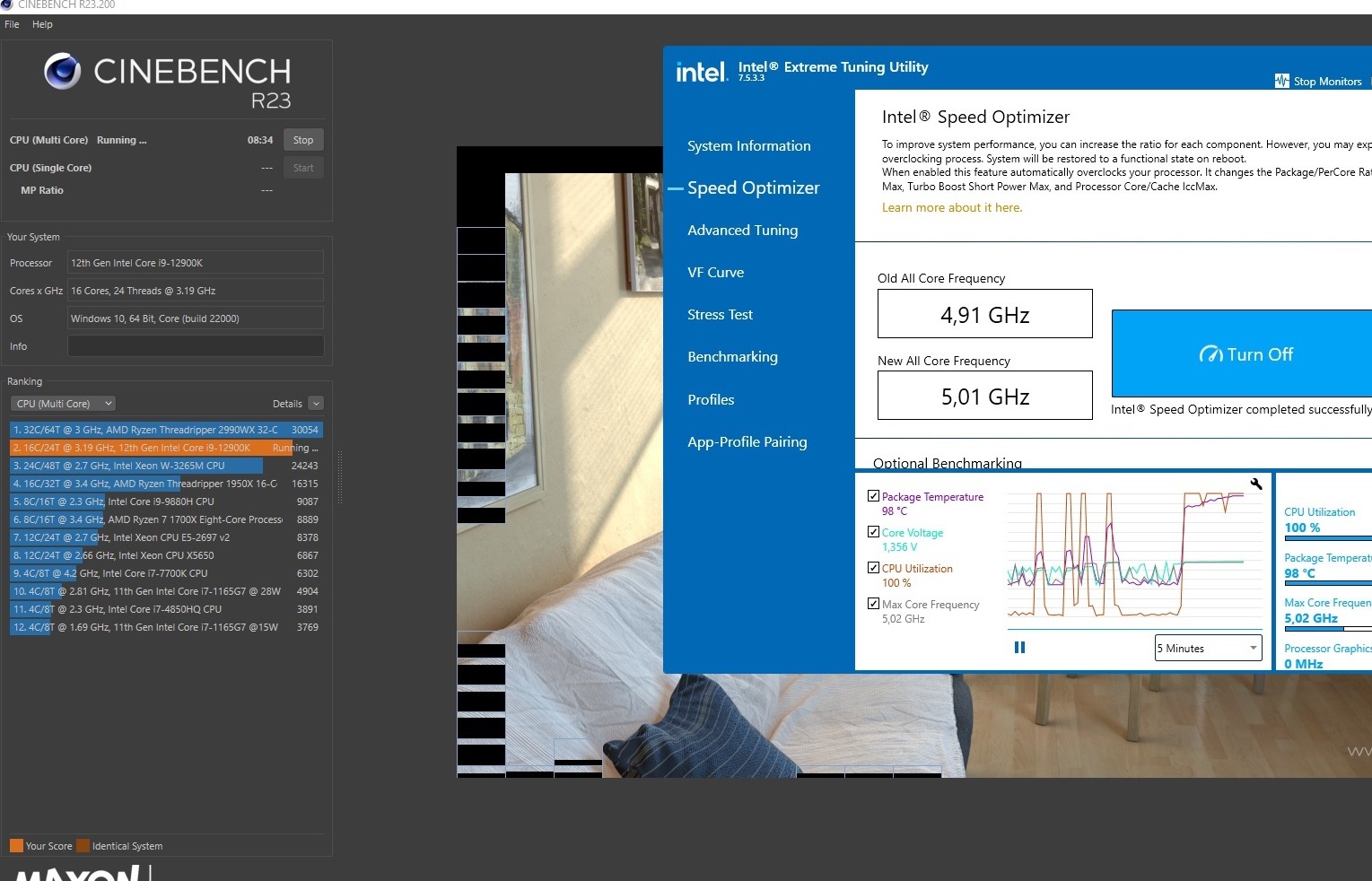
These three keys give us a fundamental context, of how to check the temperature, but we're not done yet.
We must add other essential keys that will allow us to close all the information we need to properly measure, and also interpret, the temperature of your CPU.
The first is the room temperature, although this is only relevant when we are in times with very high temperatures, as they can affect the capacity of the cooling system, causing additional overheating, with an increase in the temperature of its CPU.
Next we have the workload to which we subject the CPU, an issue that we talked about at the beginning of the product.
If we subject the CPU to a very light load, it is normal for it to record very low temperatures.
Besides, It is also very normal for its temperatures to skyrocket if we maintain a workload that uses it to its full potential..
A CPU may register an average of 60 degrees under intensive single-thread load, but reach 85 degrees when used for an hour under 100% load. Both values would be normal.
We must also keep in mind that to make a game Not in all cases is it equivalent to having the CPU at a hundred and one percent of use.
There are levels where this is the case, such as when we use processors that have only 4 threads, and in certain cases 4-core, 8-thread processors can also reach 100% utilization when running some games, but when using 6-core, 12-thread processors (or more) their utilization rate will never be as high.
To put them at 100% of employment, it will be necessary use concrete evidence, as an example Cinebench R23.
This test is one of the best ways to measure the temperature of a processor under simple load conditions and the 100%, and will also give us an idea of its performance.
To finish
It is also necessary to take into account the characteristics of each architecture, and of each type of processor, since there are designs that They are ready to work pushing the consumption and temperature margin to the limit., all in an effort to provide the maximum possible performance by pulling the turbo mode escalation, which works actively.
For example, a processor like the Intel Core i9-12900K has a very aggressive turbo mode and a maximum junction temperature of one hundred degrees.
This chip It can exceed 90 degrees and work completely normally, while it will actively adjust the working temperatures to avoid damage and to sustain the highest possible performance.
This is what I have also told you in several analyses, that most of the recent processors trigger the turbo mode to achieve the maximum possible performance, which causes them to reach very high temperatures, but once they reach that peak they begin a stabilization process to avoid problems. It is not something we should be worried about.
View CPU temperature Windows 10 – How to interpret the results and why it is good to actually measure the CPU temperature

Each CPU can achieve a different temperature under the same performance test for very different reasons.
We have already named many of them, but two of the most essential, and those that are least often taken into account, are the architecture and the maximum number of cores and threads.
An architecture that is much more advanced than another will generally be much more efficient in terms of performance per watt, and will have much lower temperatures. controlled.
At the same time, 2 processors using a same architecture but have a different number of cores and also threads They will also record different temperatures when working at full load.
For example, a Ryzen 3 3300X, which only has 4 cores and 8 threads, is much cooler than a Ryzen 9 3950X, which has 16 cores and 32 threads.
It is completely normal, since the difference between the two is colossal.
Also, a CPU with fewer cores may experience much higher temperatures due to the fact that it is working at a higher frequency.
I wanted to clarify this because it is essential when interpreting the results when we are going to measure the CPU temperature.
Analyzing temperatures.
Continuing with the previous example, A temperature of 85 degrees is going to be abnormal for a Ryzen 3 3300X, but it can be completely usual for a Ryzen 9 3950X.
That is why context is so essential, as is understanding the characteristics of the CPU whose temperature we want to measure.
As far as the results we get are concerned, the single-thread performance test is an indication that serves as an approximate reference of the temperatures that a CPU can reach with a fast multi-thread load.
A much more intensive multi-threaded test now lets us test the security of the CPU, but the perfect thing to do a full check is master it at a load of 100% for at least 30 minutes.
That is why it is good to truly measure the temperature of a CPU by performing tests of different intensities, because we will be able to see how it behaves, if it registers any anomaly in terms of performance or temperature, and If you suffer from any serious problem security, such as crash, reboot issue, or blue screen of death.

Doing the testing.
Not carrying out these tests can end up giving us many scares, and I can give you an example.
A few years ago a popular person mentioned to me that he had taken his Ryzen 7 2700X at 4.3GHz on each and every core, and it worked fine.
I asked him if he had tried it thoroughly and he said yes, he had used “certain games” and that was great.
In the end it turns out that I had only tested it with Destiny 2, a game that requires very little central processing unit, and that In relation to this, he tested a much more rigorous title and the device kept hanging.
Under normal use, it is very difficult for us to use a CPU like the Ryzen 7 2700X at a hundred and one percent of use, but there are games and apps that can be demanding, and for this reason it is advisable to take our central processing unit a little to the maximum, to check that it is capable of supporting without problems, and that will not give us any trouble.
On the other hand, this will also allow us to check that the cooling system we use is capable of keeping the temperatures of our processor under control.
Ok, so how should I interpret the results when measuring the CPU temperature?
You have to put them in context with everything we have said, and be clear about where the limits of your central processing unit are.
For example, a Core i9-12900K has that 100 degree limit, but a Ryzen 9 5950X has a maximum temperature of 90 degrees.
In the first case, a temperature of 95 degrees under extreme workload sustained over a long period of time would be acceptable, but that temperature would not be acceptable in the Ryzen situation.
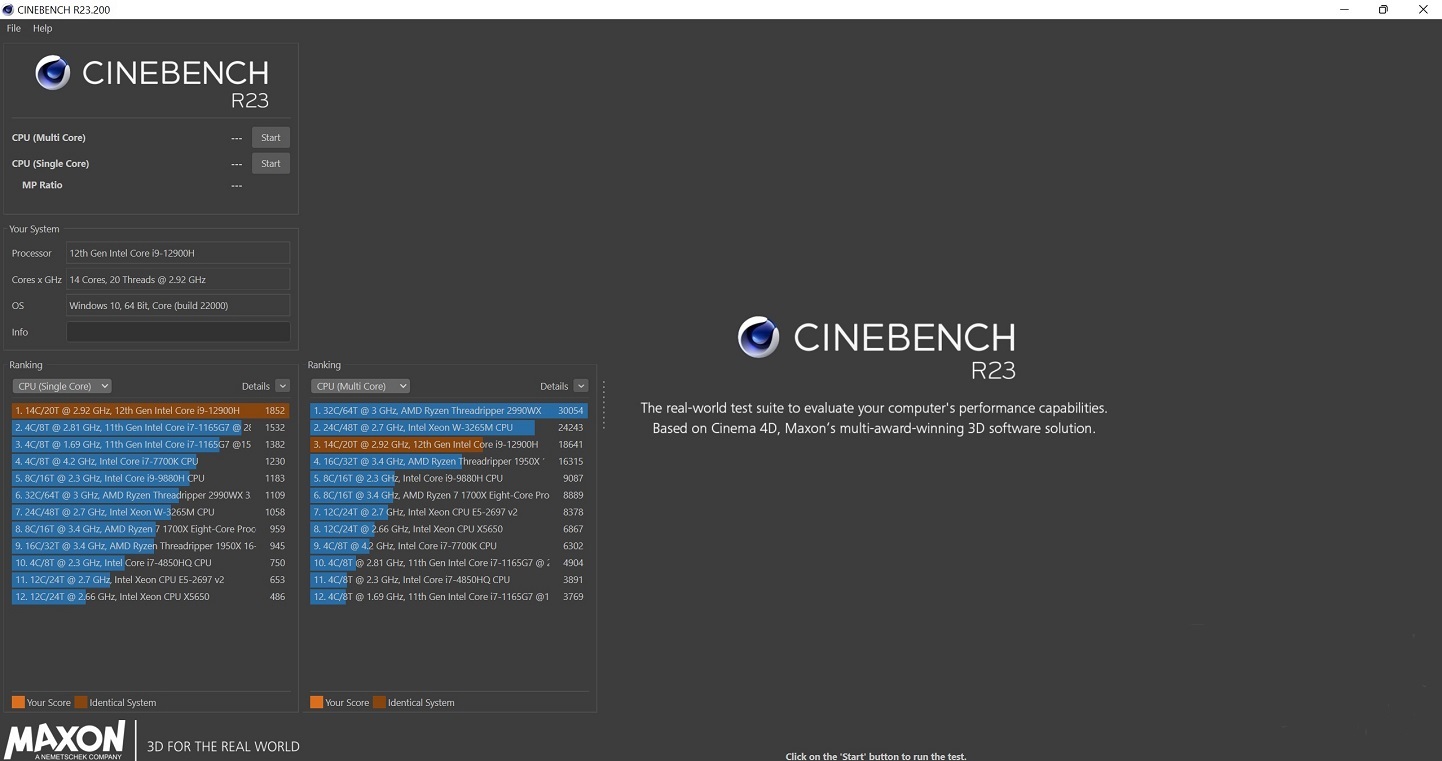
On the other hand, it is also a good initiative. that you can take advantage of the results of a performance test like Cinebench R23 to give you even more context for monitoring.
You can compare the results your CPU obtained with the databases that are available on Internet, and assess whether these performance results are normal or below what they should be.
This could indicate a serious problem, usually temperature-related, although possibly also power-related.
I would like to return to an essential theme: Don't obsess over what you've read on the Internet, and I mean things like "my CPU runs at 60 degrees, it's not normal for yours to go up to 80 degrees."
In addition, the comparison, to be validated, the computer being monitored, should be of equal hardware and software, the motherboard, components PC, graphics card with same GPU, hard drive and temperature of each CPU measured with the same monitor hardware, fan speed with the same rotation, equivalent thermal environment, etc.
That a modern processor works at 80 degrees may be perfectly normal, in fact in some cases it can even be an excellent result.
Many of those comments you will find on the Internet are based on tests carried out with a load on the central unit of prosecution of only the 30% or the 40%, so don't worry and follow the advice we have just given you in this guide.
Finally, and as a reference, be clear that In no case is it positive for a processor to reach, or stay, in the 100 degree range..
If this happens, it is best to stop the test and consider getting a better cooling system, or if you overclocked, back off, as you could drastically shorten the life of the processor, especially if you have raised the voltages to keep said overclock.
View CPU temperature Windows 10 – Other applications as an option to control the CPU temperature.
MSI Afterburner
MSI Afterburner is a handy overclocking utility for MSI graphics cards. Key features include GPU/Shader/Memory clock tuning, advanced GPU speed, and more. fan and GPU voltage control. It supports NVIDIA and ATI cards, as well as GPUs Integrated graphics on AMD APU series. MSI Afterburner is an overclocking utility for graphics cards MSI. Its main features include CPU clock speed adjustment/GPU/memory, advanced fan speed and GPU voltage control. Supports NVIDIA and ATI cards, as well as graphics cards integrated graphics on AMD processors APU.
HWiNFO
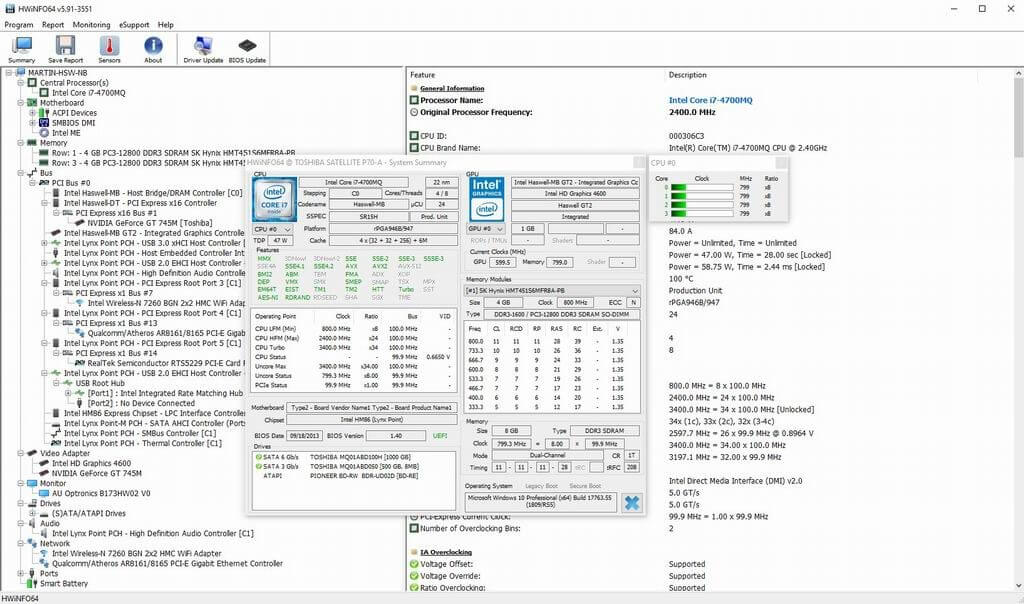
HWiNFO is an all-in-one solution for analyzing and monitoring hardware compatible with a wide range of operating systems (DOS, Microsoft Windows 95 – Windows 11, WinPE) and hardware platforms (x86, x64, ARM). This application RTSS is a custom version of HWiNFO specially optimized for use with MSI Afterburner and RivaTuner Statistic Server. You can download it here: download. If you don't know what to do with it, you can find more information here: about-software. If you have any questions regarding MSI Afterburner / RTSS support, please send an email to support@msi.com MSI Afterburner 4.6.2 Final – Download for PC Free 9/10 – Download MSI Afterburner for PC Latest Version Free.
HWMonitor
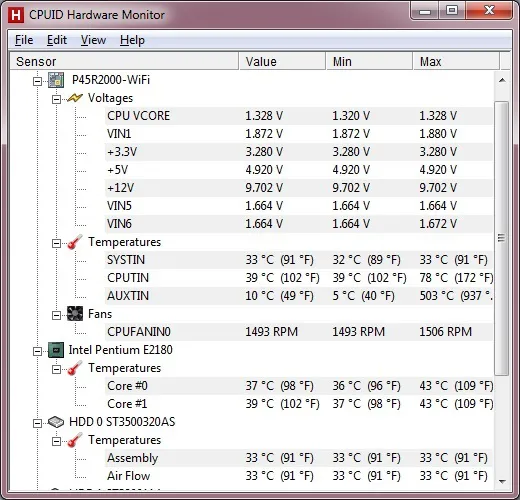
HWMonitor is a hardware monitoring program that reads the main health sensors of PC systems: voltages, temperatures, power, currents, fan speeds, usage, clock speeds… The program handles the most common sensor chips, such as the ITE® IT87 series, most of the integrated circuits Winbond® and others. There is a version for Linux called HWSensors. To install it with yaourt: yaourt -S hwmonitor
The program handles:
- Supervision of hardware at CPU and GPU level
- LPCIO chips with monitoring functions (ITE® IT87 series, Winbond® and Nuvoton® ICs)
- modules of memory with thermal sensors
- SSD / hard drives through SMART
- batteries
- and more…
Open Hardware Monitor
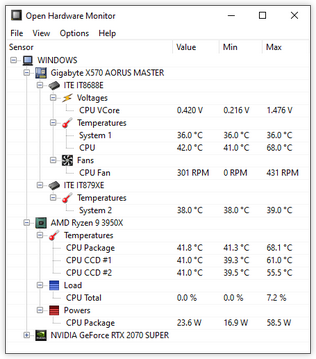
Open Hardware Monitor is a free, open source software that monitors a computer's temperature sensors, fan speeds, voltages, load, and clock speeds of the computer's components. Hardware Monitor displays the information obtained in a simple and easy-to-use window.
Open Hardware Monitor supports most hardware monitoring chips found on today's motherboards. CPU temperature can be monitored by reading the CPU temperature sensors. Intel processor core and AMD. Sensors from ATI and AMD video cards can be displayed. Nvidia, as well as the temperature of the SMART hard drive. The values monitored They can be displayed in the main window, on a customizable desktop widget, or in the system tray. software Free Open Hardware Monitor runs on Microsoft Windows XP/Vista/7/8/8.1/10 32-bit and 64-bit and any x86-based Linux operating system without installation.
Download Open Hardware Monitor 0.9.6